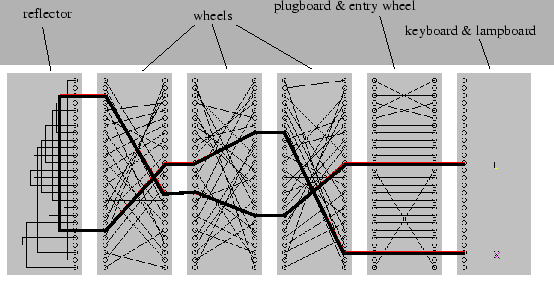
The Enigma machine uses a series of rotors to encrypt messages. Each rotor is a disk with 26 positions, corresponding to the letters of the alphabet. When a key is pressed, an electrical current passes through the rotors, which substitute the input letter with another letter based on the rotor's internal wiring. The rotors then rotate, changing the substitution pattern for the next key press.
The rotor mechanism can be abstracted using an assignment matrix. This matrix represents the wiring of the rotor, where each row corresponds to an input letter, and each column represents the output letter after substitution. For example, if the letter 'A' is substituted with 'D', the matrix would have a 1 at the position (A, D) and 0 elsewhere in that row. By using such a matrix, we can simulate the rotor's behavior programmatically, allowing for flexible and efficient encryption and decryption processes.
Because Enigma machines use multiple rotors, the assignment matrix is applied iteratively. The output of one rotor becomes the input of the next rotor, and so on. The final output is the result of passing the input through all rotors in sequence.
From a random setting of our data, can we use a neural network or Linear Algebra to learn the assignment matrix of the rotors?
To set up a virtual environment and install the required packages with pip, follow these steps:
- Create a virtual environment:
python3 -m venv env- Activate the virtual environment:
- On Windows:
.\env\Scripts\activate
- On macOS and Linux:
source env/bin/activate
- Install the required packages:
pip install -r requirements.txt- Put your dataset into the DataModule.py file.
- This details how to load your data onto the server. An example is given for Enigma, generating a random encoding.
- Edit the model files.
- build or load an existing model in the init function
- Include the logic for the forward, train_step, and optionally validation_step too.
- This is written for you! More info for code structure at Pytorch-lightning: https://github.com/Lightning-AI/lightning/tree/master/examples/convert_from_pt_to_pl
- Deploy a Sweep, and launch an Agent if you want to test everything!
- This is done by running '''python CreateWandBSweep.py'''
- Have a look at the files generated! Are they what you expected? what kind of constraints can you try putting on the problem?
- If you want to ask any questions, please use the SLIDO code on the board!
- All runs will default log to W&B, which we'll use to identify and share solutions during the Lab!