Django models translation on fly 🛸️
This project was initiated, promoted and accompanied by winePad GmbH. All development based on ideas, experience and financing by winePad GmbH (winePad.at).
The background and objectives of this projects are described here
An Application for dynamic translation of existing Django models into any number of languages.
- without need to change existing model classes
- without need to reboot servers
- without changing the use of translated fields
- ready to work after install and indicated in INSTALLED_APPS
- fully integrated in Django admin
pip install django-tof
python manage.py migrate tof
# settings.py
...
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
'tof',
...
]Don't forget to do if it necessary python manage.py collectstatic
- In the simplest use case django-tof allows you to store translation into the current language. You don't need special settings for this, just add this field into admin panel to the "Translatable fields" model. In this case if current language is 'en', then the value saved in the model will be displayed only if the current language is 'en'.
- If you need to support a certain number of languages and add them at the same time, you can use
TofAdmin. Using theclass CustomModelAdmin(TofAdmin)will cause the translated fields (added to the "Translatable fields") will be able to specify a specific language. At the same time, it is possible to leave some fields in the previous form by specify them inTofAdminwith attributeonly_current_lang = ('description', ).
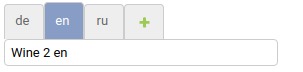
- You can also use inline translation submission forms. To do this, specify admin class (always inherited from "TofAdmin")
inlines = (TranslationTabularInline, )orinlines = (TranslationStackedInline, )
Like a standard using, but it is possible to get a specific translation.
from django.utils.translation import activate
activate('en')
book = Book.objects.first()
book.title # => Title en
book.title.de # => Title deThe value for these variables can be specified in your settings.py
DEFAULT_LANGUAGE: default "en" - Default language is stub, used if not other translations is found.
FALLBACK_LANGUAGES: default {SITE_ID: ('en', 'de', 'ru'), 'fr': ('nl', ),} - Determinate the order of search of languages for translation if the translation is in desired
no language. The key can be SITE_ID, None or language.
The processing order is this, if a translation into current/requested language is not found, then first we checked by the language key, if there is, looking translations for requested languages, if not - we take the SIDE_ID key. For example:
- if current language "fr", then searching order will be next: "fr" -> "nl" -> DEFAULT_LANGUAGE -> then if there is an original value that was before the declaration of this field like translatable.
- if current language "en", then searching order will be next "en" -> "de" -> "ru" -> DEFAULT_LANGUAGE -> then if there is an original value that was before the declaration of this field like translatable.
DEFAULT_FILTER_LANGUAGE: default "current" - Indicates in which translations search/filter values. May be in the next forms __all__, current, ['en', 'de'], {'en', ('en', 'de', 'ru')}
current- if this value is assigned, the filtering is occurs only on the translation into the current language. This is a default value.__all__- if this value is assigned, the filtering is occurs for all translations.['en', 'de']- if this value is assigned, the filtering is occurs according to translations of the specified languages.{'en', ('en', 'de', 'ru')}- if this value is assigned, the filtering is occurs according to translations of languages received by the key of current language.
CHANGE_DEFAULT_MANAGER: default "True" - Changing the default manager of the model. If it True, then standard manager is transferred into class attribute "objects_origin", and "objects" becomes the standard manager inherited from standard with adding the functionality that recognized translated fields and takes into account settings from DEFAULT_FILTER_LANGUAGE.
- Python (>=3.6)
- Django (>=2.2)
- Fork this project
- Clone the repo
- Create new branch
- Change directory
example_project - You can use pyenv to select the version of python
pyenv local 3.8.0 - We are using poetry
- Run:
poetry env use pythonto use your python version. - Run:
poetry installto install all requirements. - Run:
poetry shellfor activation virtual environment. - Run:
python manage.py runserverto start the development server.