⚠️ NOTICE⚠️ : This repository has been archived. The code has been moved to thekalerepository, where it is maintained under thelabextensionfolder.
This JupyterLab extension provides a Kubeflow specific left area that can be used to deploy a Notebook to Kubeflow Pipelines. The UI is just high level component designed to let the user annotate Notebook metadata and Cells metadata easily and visually. In order to convert the notebook to a Kubeflow Pipeline workflow and have it run in KFP, Kale needs to be installed in the same Python environment as the running Notebook Kernel.
# install jupyter lab
pip install jupyterlab==1.1.1
# install kale: see instructions in Kale repository
# ...
# install the extension
jupyter labextension install kubeflow-kale-launcher
# verify extension status
jupyter labextension list
# run
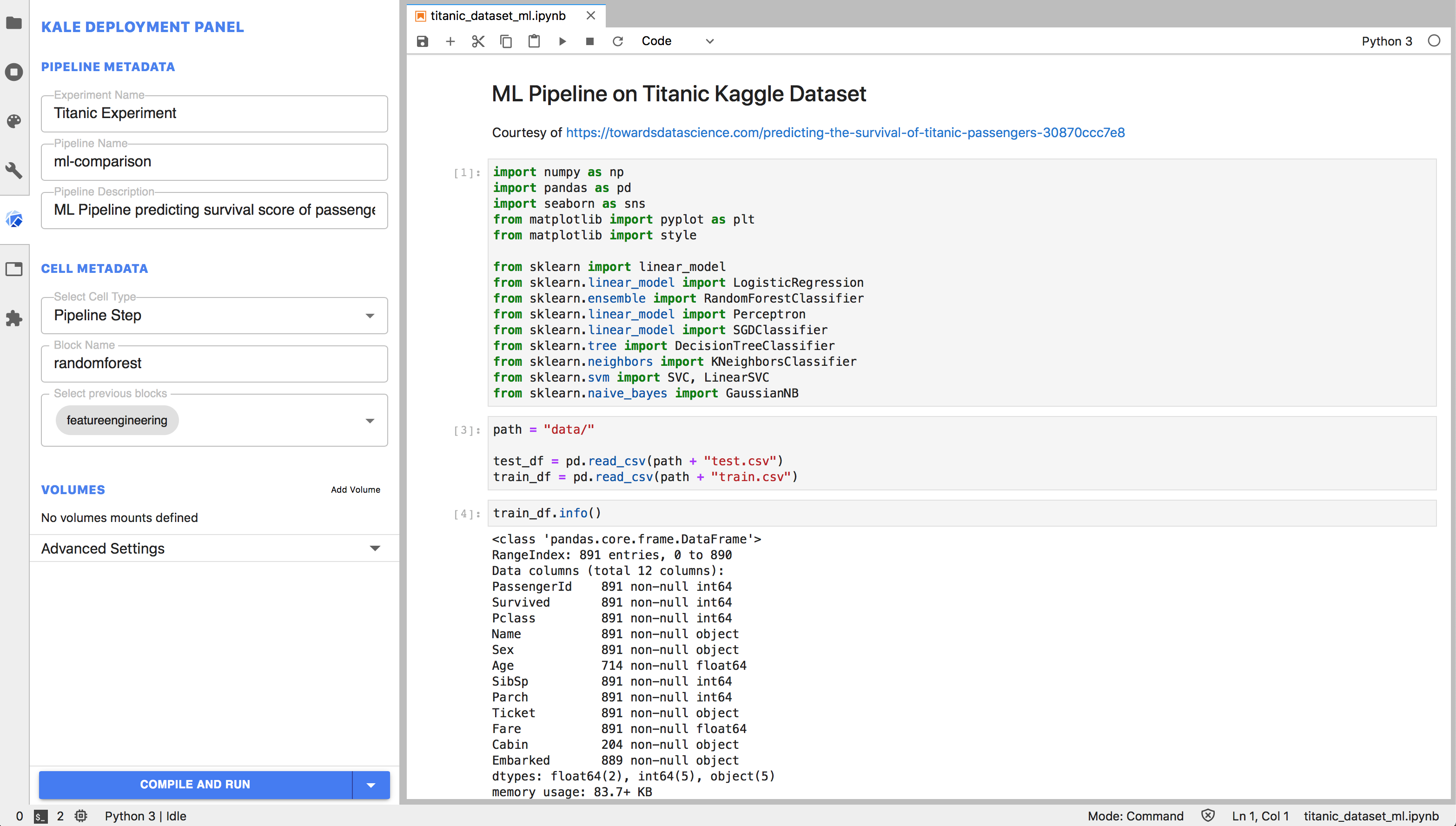
jupyter labKale Launcher UI lets you update Notebook and Cells metadata according to Kale spec. The extension reads and saves Notebook metadata automatically, keeping a consistent view of the Notebook spec. You don't have to worry about manually saving the Notebook, the extension will write any new changes automatically.
When clicking the big blue run button, Kale will be run in the background over the active Notebook and perform the required action based on the button option selected.
The Launcher is able to invoke Kale in the background by programmatically executing shell commands in the Kernel environment. Specifically, it will run:
kale --nb <current_active_notebook_name> [--upload_pipeline] [--run_pipeline]
To build and run the extension in dev mode, first clone the repository in your local machine.
# Move to repository folder
cd jupyterlab-kubeflow-kale
# Install dependencies
jlpm install
# Build the extension. This will generate a dist/ folder with build files
jlpm run build
# Add the extension to jupyterlab.
# Be sure to uninstall any other version first (e.g. npm kubeflow-kale-launcher package)
jupyter labextension install .When developing, you can run jlpm in watch mode to incrementally compile the new changes:
jlpm run watch
And run JupyterLab in watch mode to load the new compiled version:
jupyter lab --no-browser --watch
This repository uses husky to set up git hooks.
For husky to function properly, you need to have yarn installed and in your
PATH. The reason that is required is that husky is installed via
jlpm install and jlpm is a yarn wrapper. (Similarly, if it was installed
using the npm package manager, then npm would have to be in PATH.)
Currently installed git hooks:
pre-commit: Run a prettier check on staged files, using pretty-quick