This repository has been archived by the owner on Feb 22, 2024. It is now read-only.
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 6
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
1 parent
82c7890
commit 52d9781
Showing
65 changed files
with
314,326 additions
and
102,960 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,143 @@ | ||
| # Analytics with Python Workflow for Democratized Solution for RecSys 2021 - Training | ||
|
|
||
| ## Overview | ||
| The [Analytics with Python Workflow](https://github.com/intel/recommender-system-with-classical-ml) contains an end-to-end workflow for large-scale predictive analysis in tweet engagement prediction. It is originated from intel's democratization solution for the ACM RecSys-2021 challenge and is designed to be generalizable for a wide range of binary classification tasks on large-scale tabular dataset. The top 3 features of this workflow includes | ||
|
|
||
| - distributed data preprocessing, XGBoost training and hyperparameter optimization | ||
| - rich data processing & feature engineering techniques for large and heterogeneous input data (from 20 original features to 262 training features) | ||
| - simple but effective training strategies on CPU, e.g. training set subsampling, model stacking | ||
|
|
||
| ## How it Works | ||
|
|
||
| * As with all machine learning tasks, there are 2 phases in the T4 workflow: Training and Inference. we use 2-stage **model stacking** for training. Stacking is an ensemble method, in which we train new models that uses the prediction of other models as an input. | ||
| * As shown in the diagram, stage-1 models are trained using the stage-1 training features and then used to make predictions on the validation features. Next, these predictions are merged into the validation features and used as additional features for stage-2 training. We also split the original validation features into 2 part: one for training and one for validation. The final training results are evaluated on the stage-2 validation features. | ||
| * we use **training set subsample** for training, where only 8.3% of the original training set is used for training | ||
| * we include **2 ecosystems in one workflow**. The workflow is designed to be easy-to-use for people with different background. If you are a data engineer who is familiar with frameworks born out of Hadoop ecosystem, you can choose to run the whole workflow on Hadoop and Spark Cluster. If you are a data scientist who is used to Python ecosystem, then you can choose to run it on Modin and Ray, where Modin is for distributed data preprocessing and Ray for distributed XGboost training. But if you want to use Spark for data preprocessing and Ray for training or Modin for data preprocessing and Spark for training, it is also possible with the workflow. | ||
|
|
||
| 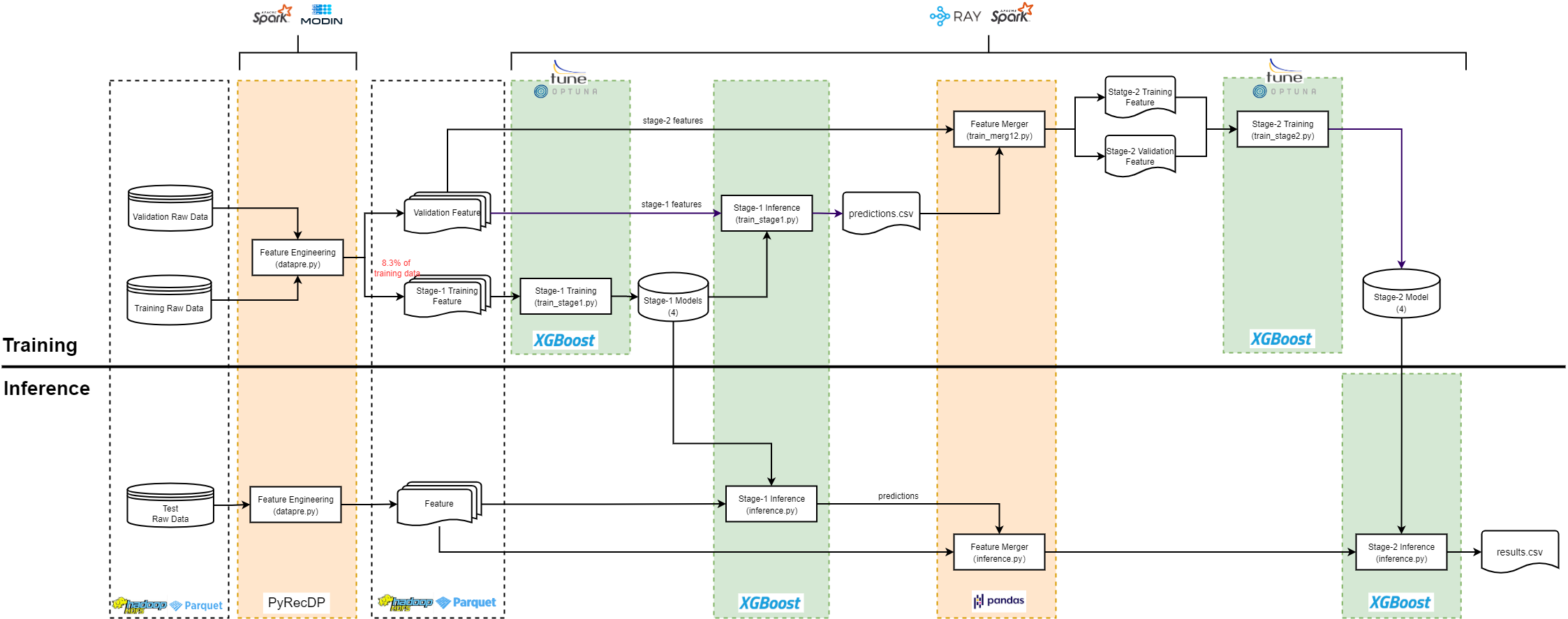 | ||
|
|
||
| The T4 workflow contains extensive data processing & feature engineering techniques. The image below gives an overview of the major data preprocessing steps for stage-1 training. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Data Preprocessing Overview | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| Regarding stage-2, the only difference is that stage-2 data preprocessing includes one more feature engineering technique called Count Encoding and it also split data into train and validation sets. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Get Started | ||
|
|
||
| ### **Prerequisites** | ||
| #### Download the repo | ||
| Clone [Recommender System with Classical ML](https://github.com/intel/recommender-system-with-classical-ml) Repository. | ||
| ``` | ||
| git clone https://github.com/intel/recommender-system-with-classical-ml | ||
| cd recommender-system-with-classical-ml | ||
| git checkout mlops-release | ||
| ``` | ||
| #### Download the datasets | ||
| To download the challenge dataset, please follow the instructions on the official website of [RecSys2021 Challenge](http://www.recsyschallenge.com/2021/). We are not allowed to transfer the challenge dataset or host it publicly on the web. | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| | **Type**: | **Format** | **Size** | **Shape** | ||
| | :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- | ||
| | Training Dataset | 201 parquet files | 231 GiB (1.2 GiB each) | (63565312, 25) | ||
| | Validation Dataset | 1 csv file | 6.8 GiB | (17354112, 25) | ||
|
|
||
| To make it easier for users to test the workflow, we include a python script to make synthetic data, which is under the path `src/data_loader`. You can use the following command to generate synthetic data: | ||
| ```bash | ||
| python src/data_loader/generate_data.py --save_path [SAVE_DATA_PATH] | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ### **Docker** | ||
| Below setup and how-to-run sessions are for users who want to use provided docker image. | ||
| For bare metal environment, please go to [bare metal session](#bare-metal). | ||
| #### Setup | ||
|
|
||
| ##### Pull Docker Image | ||
| ``` | ||
| docker pull intel/ai-workflows:analytics-with-python | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| #### How to run | ||
|
|
||
| To quickly set up a working environment if you are in the single-node & single-container mode, please follow the steps below. For other modes of training and step-by-step directions please follow the Interactive Training section of this guide. | ||
|
|
||
| (Optional) Export related proxy into docker environment. | ||
| ```bash | ||
| export DOCKER_RUN_ENVS="-e ftp_proxy=${ftp_proxy} \ | ||
| -e FTP_PROXY=${FTP_PROXY} -e http_proxy=${http_proxy} \ | ||
| -e HTTP_PROXY=${HTTP_PROXY} -e https_proxy=${https_proxy} \ | ||
| -e HTTPS_PROXY=${HTTPS_PROXY} -e no_proxy=${no_proxy} \ | ||
| -e NO_PROXY=${NO_PROXY} -e socks_proxy=${socks_proxy} \ | ||
| -e SOCKS_PROXY=${SOCKS_PROXY}" | ||
| ``` | ||
| To run the pipeline, follow below instructions outside of docker instance. | ||
| ```bash | ||
| if ! docker network inspect hadoop | ||
| then | ||
| docker network create --driver=bridge hadoop | ||
| fi | ||
|
|
||
| export OUTPUT_DIR=/output | ||
| export DATASET_DIR=<Path to Dataset> | ||
|
|
||
| docker run \ | ||
| -a stdout $DOCKER_RUN_ENVS \ | ||
| --net=hadoop \ | ||
| -p 8088:8088 \ | ||
| -p 8888:8888 \ | ||
| -p 8080:8080 \ | ||
| -p 9870:9870 \ | ||
| -p 9864:9864 \ | ||
| -p 4040:4040 \ | ||
| -p 18081:18081 \ | ||
| -p 12345:12345 \ | ||
| --name hadoop-master \ | ||
| --hostname hadoop-master \ | ||
| --volume ${OUTPUT_DIR}:${OUTPUT_DIR} \ | ||
| --volume /${DATASET_DIR}:/mnt/data \ | ||
| --volume $(pwd)/tmp:/mnt \ | ||
| --volume $(pwd)/analytics-with-python/config:/mnt/config \ | ||
| --volume $(pwd)/analytics-with-python:/mnt/code \ | ||
| --privileged --init -it --rm \ | ||
| --workdir=/mnt/code \ | ||
| recsys \ | ||
| /bin/bash -c \ | ||
| "service ssh start && \ | ||
| /mnt/code/run-all.sh" | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ##### Interactive Training | ||
|
|
||
| | **Training Type**: | | ||
| | :--- | | ||
| | [Single-Node & Single-Container Version](https://github.com/intel/recommender-system-with-classical-ml#:~:text=Installation-,Single%2DNode%20%26%20Single%2DContainer%20Version,-Prerequisites) | | ||
| | [Multi-Node & Multi-Container Version](https://github.com/intel/recommender-system-with-classical-ml#:~:text=as%20shown%20below%3A-,Multi%2DNode%20%26%20Multi%2DContainer%20Version,-Prerequisites) | | ||
|
|
||
| | **Usage Mode**: | | ||
| | :--- | | ||
| | [Data Preprocessing](https://github.com/intel/recommender-system-with-classical-ml#usage:~:text=Usage-,Data%20Preprocessing,-On%20the%20master) | | ||
| | [Training](https://github.com/intel/recommender-system-with-classical-ml#usage:~:text=mnt/data/processed_data-,Training,-single%2Dnode%20xgboost) | | ||
|
|
||
| ### **Bare Metal** | ||
| For bare metal environment, please go to [Bare Metal Installation Doc](https://github.com/intel/recommender-system-with-classical-ml/blob/main/docs/bare-metal-installation.md) | ||
|
|
||
| ## Recommended Hardware | ||
| The hardware below is recommended for use with this reference implementation. | ||
| - one host machine that has comparable configurations as follows | ||
|
|
||
| | **Name**: | **Description** | ||
| | :--- | :--- | ||
| | CPU | Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8380 CPU @ 2.30GHz (160 vCPUs) | ||
| | Free RAM | 460 GiB/503 GiB | ||
| | Disk Size | 1.5 TB | ||
| | Disk Type | Sata-INTEL_SSDSC2KB019T7_PHYS7412006U1P9DGN | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| **Note:** <br>It is also possible to run through the code using a machine with a smaller RAM, but then you will need to manually set the `spark.driver.memory` to a value that your machine can handle in the `datapre.py` script. But if you have not enough free disk space, Spark/Hadoop will have trouble processing all the raw data. In this case, you can consider reducing the data amount for preprocessing (note: it would affect the prediction accuracy) or use the already processed data to run the training job. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Useful Resources | ||
| [Intel® AI Analytics Toolkit (AI Kit)](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/developer/tools/oneapi/ai-analytics-toolkit.html) | ||
|
|
||
| ## Support | ||
| Please refer to [Hadoop Traps & Pitfalls](https://github.com/intel/recommender-system-with-classical-ml/tree/v1.0.1/docs/hadoop-traps-pitfalls.md) and [Spark Traps & Pitfalls](https://github.com/intel/recommender-system-with-classical-ml/tree/v1.0.1/docs/spark-traps-pitfalls.md) for more information. |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,18 @@ | ||
| DATASET_DIR ?= /data/recsys2021 | ||
| FINAL_IMAGE_NAME ?= recsys-challenge | ||
| OUTPUT_DIR ?= /output | ||
|
|
||
| recsys-challenge: | ||
| ./analytics-with-python/hadoop-folder-prep.sh . | ||
| if ! docker network inspect hadoop ; then \ | ||
| docker network create --driver=bridge hadoop; \ | ||
| fi | ||
| @DATASET_DIR=${DATASET_DIR} \ | ||
| FINAL_IMAGE_NAME=${FINAL_IMAGE_NAME} \ | ||
| OUTPUT_DIR=${OUTPUT_DIR} \ | ||
| docker compose up recsys-challenge --build | ||
|
|
||
| clean: | ||
| sudo rm -rf tmp | ||
| docker network rm hadoop | ||
| DATASET_DIR=${DATASET_DIR} CONFIG_DIR=${CONFIG_DIR} docker compose down |
Oops, something went wrong.