The purpose of this repo is to provide an abstract and minimalist traffic simulation using OpenStreetMaps and OSMnx which can simulate traffic on any road network from OSM.
I train a three-layer, linear learning architecture using the Keras and Tensorflow open APIs. This model optimizes a car's route to its destination by deciding between two options: (1) the original Dijkstra's shortest path between its origin and destination or (2) a detour path around the traffic light in its route having the longest light time.
The optimization algorithm in learn.py can be implemented for one car in the system. This car will learn its pre-configured route to shortest-time by trying the alternate route. I've written my own re-routing algorithm for this project, leveraging OSMnx.
The learning algorithm uses Q-learning with epsilon greedy techniques, and a dynamic reward scheme based on a car's time-to-complete. If a car took longer to reach its destination after changing routes, it receives a negative reward proportional to the time difference in routes.
After customizing desired parameters in the source code, run the artist scratch file with:
python artist.pyto render .mp4 or .html movies of a traffic simulation.
You can select a car in the source code as the learning agent (i.e. any number 1-N, where N is the number of cars desired in the simulation. Every car has a pre-configured route.) Then, run python learn.py to optimize that car's route to shortest-time.
High Performance Examples
Low Performance Examples
Simple Example of Optimization
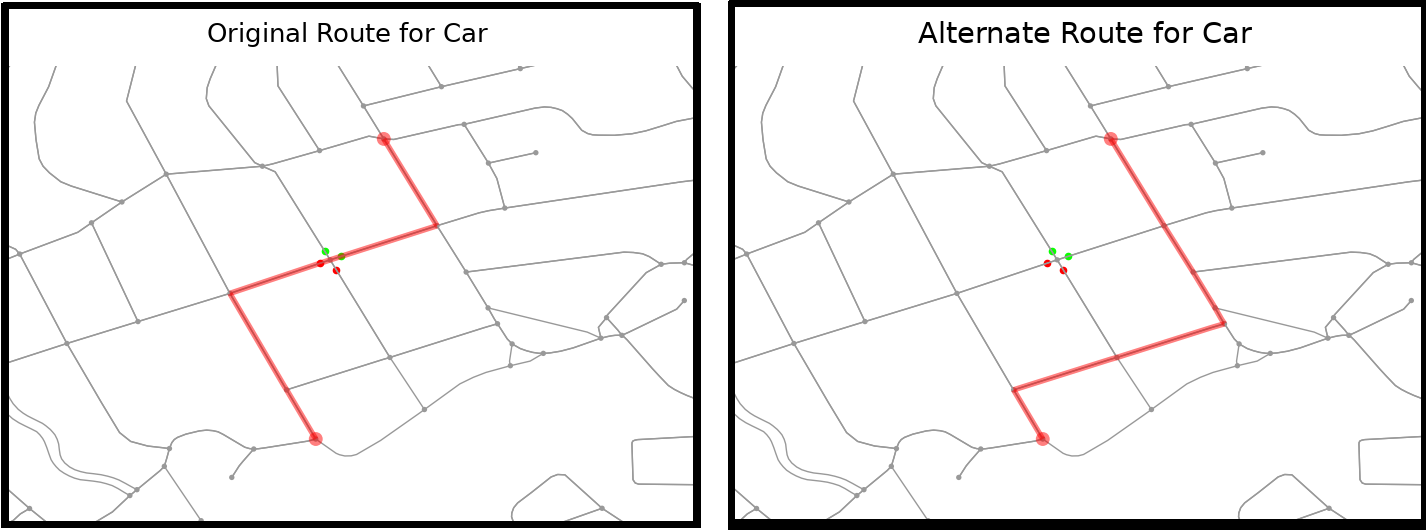 The above figure is a simple example of how a learning agent reroutes around a single traffic light.
The above figure is a simple example of how a learning agent reroutes around a single traffic light.
In the original route (left) the learning agent is in State 1. State 1 implies three criteria: (1) there are obstacle(s) in the route, (2) the detour around the most significant obstacle is short, (3) the detour contains no obstacle(s). (See the Projects tab of this repository to learn about all 10 possible states in the Markov decision chain for this project.)
The alternate route (right) is traveled in lieu of the original if the learning agent takes Action 1 (Action 0 is to do nothing).
The reward-scheme for this learning algorithm is based on whether the time to travel from A to B is the shortest of the two action possibilities. Since the alternate route above does not experience a traffic light, taking Action 1 (i.e. rerouting) will be preferred the more the learning agent performs the simulation.
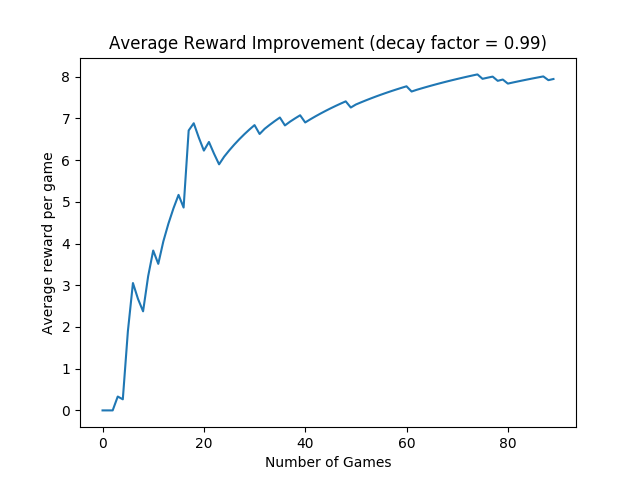
Sure enough, the average reward per game improves while training for 90-games (above).
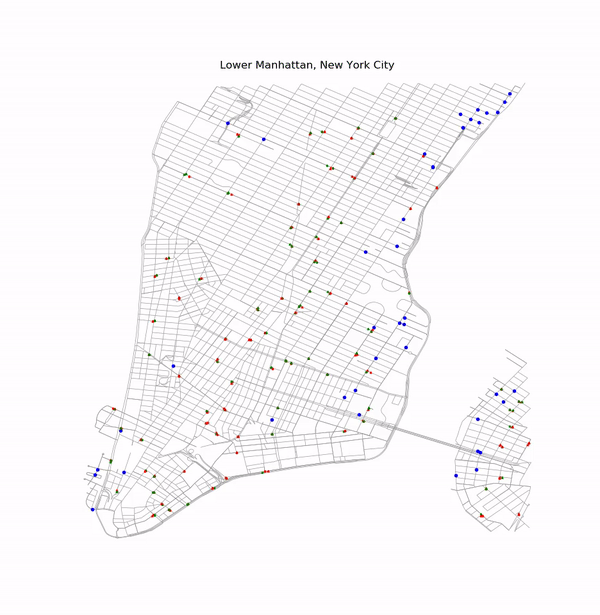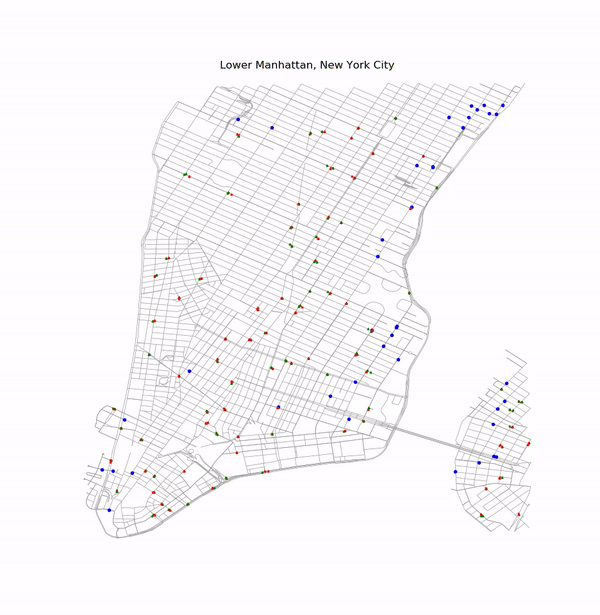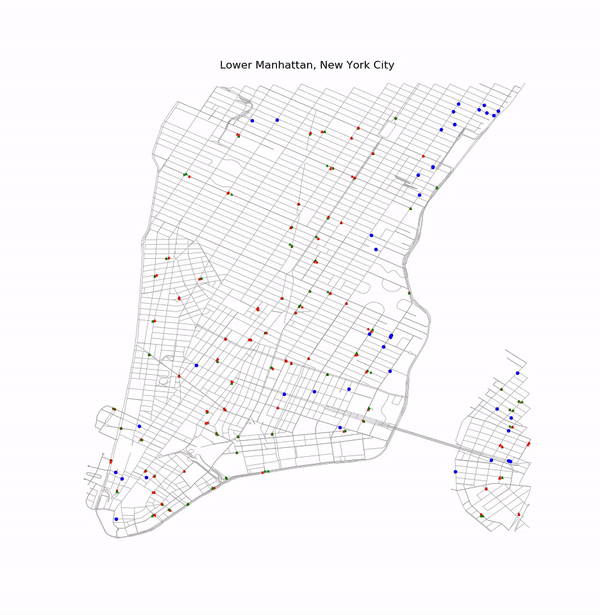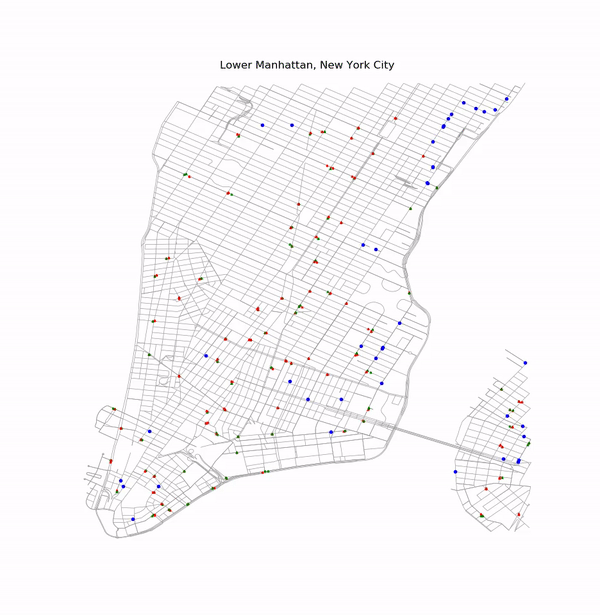
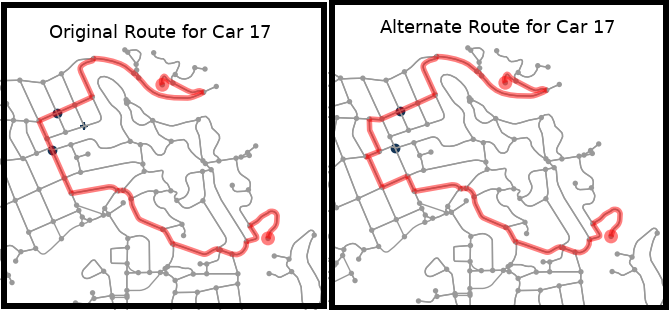
Car 17 Route and Alternate Route
There are two traffic lights (shown as blue dots) in the initial route for this car. Currently by default, the rerouting algorithm chooses to reroute around the light with the longest switch-time. In this case, it was the second light in the route which was avoided by the rerouting algorithm. Since traffic light switch-times are randomly initialized each time a map is drawn, this will not always be the case.
A note on the requirements for this code base
Installing
tensorflow 1.9.0 py36_0 (latest 12/29/2018)
conflicts with any python 3.7 (py37) environment because tf uses python >=3.6,<3.7.0a0. To handle this, I've created another environment with all the python 3.6 (py36) versions of the required packages for this code base. To install this py36 environement, see requirements_py36.txt in the requirements folder.
Once TensorFlow is upgraded to py37, the py36 requirements will be depricated.