Open-source local password manager which uses PBKDF2 hashing with random salts to store account passwords, and AES encryption in CBC mode to encrypt vault information.
The user can create accounts and save vaults to those accounts. Each account is accessed by creating a username and a password, which can later be changed. Each account can contain vaults which each have a name, description, and password. The account password is salted and hashed, and the name, description, and password of each vault is encrypted.
Password checking for minimum length is performed as well as checking a corpus of previously-breached passwords for preventing account creation of weak passwords, and warning on vault creation with weak passwords.
Random password generation and diceware password generation is a provided utility, as well as strength checking of random passwords and diceware passwords.
The minimum python version is 3.7 and sqlite3 is required (installed by default on MacOS).
Run make and follow the instructions printed out.
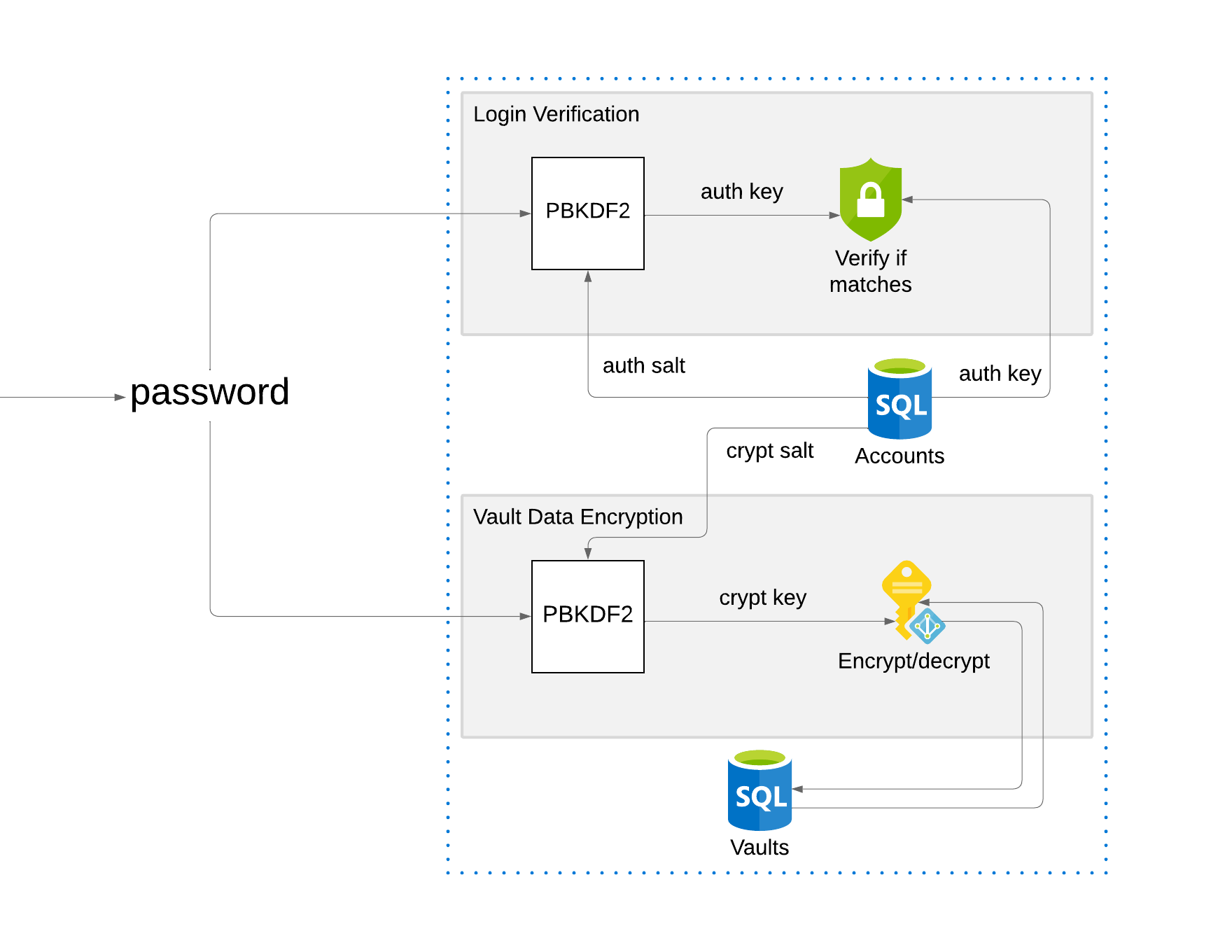
Whenever the user creates an account, two cryptographically random salts of 256 bits are created, one of them being the auth salt and the other the crypt salt. An auth key is then created by using the PBKDF2-HMAC-SHA256 algorithm with 250 000 iterations on the password and auth salt combination. A crypt key is created in the same way by applying the same algorithm to the password and crypt salt combination. This results in two different keys: the auth key, and the crypt key. The auth key, auth salt, and crypt salt are stored in the database along with the username. The crypt key and plaintext password are not stored.
Whenever the user performs an operation requiring authorization, they must provide the password. The password and auth salt from the database are used on the same password hashing algorithm to produce the auth key again. If both auth keys do not match, the user's password is incorrect. This step is only used for determining if the password is correct, and a malicious attacker could not use any information in the database to decrypt vault passwords. To decrypt vault passwords, the crypt key is needed, and is not stored in the database. To generate the crypt key, the password and crypt salt combination are used in the same hashing algorithm.
With the crypt key, the user can encrypt and decrypt vaults. Vault information is encrypted using AES in CBC mode with a cryptographically random initialization vector. The initialization vector and encrypted fields are then stored in the database. Whenever the user wishes to retrieve vault information, the crypt key and initialization vector are used to decrypt the vault information.