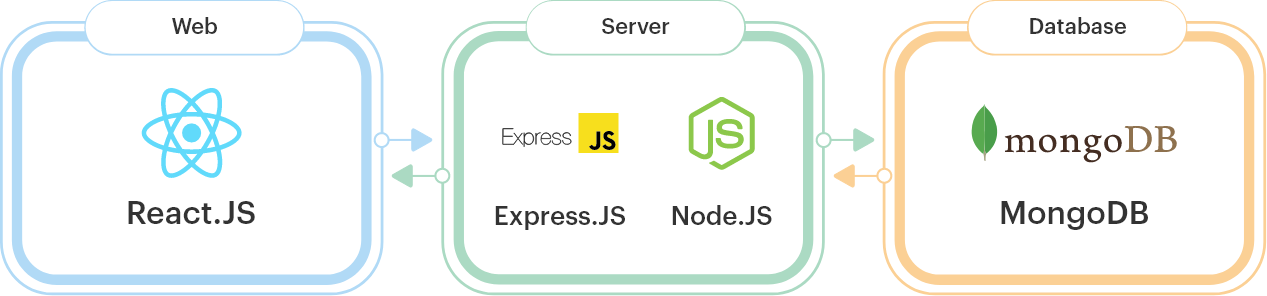
- MongoDB :- NoSQL-Database (database)
- Express.js :- Routing-MiddlewareIntegration-ErrorHandling (backend)
- React.js :- Reusable-UI-components (frontend)
- Node.js :- JavaScript-Code-On-The-Server-Side (backend)
Following installation -
- Node.js and npm
- MongoDB(locally /cloud-based solution like MongoDB Atlas)
- Code editor (eg - VS Code)
- Git (optional but recommended)
Every website has 3 pillars - Frontend Backend Database
mkdir mern-project
cd mern-project
npm init -y
npm i express mongoose body-parser cors
- express - For building the RESTfull API.
- mongoose - MongoDB object modeling tool designed to work in an asynchronous environment.
- body-parser - To parse incoming request bodies.
- cors: Middleware for enabling Cross-Origin Resource Sharing.
- Create a file server.js :
const express = require('express');
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const cors = require('cors');
const app = express();
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 5000;
// Middleware
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.use(cors());
// Routes
app.use('/api', require('./routes/api'));
// MongoDB Connection
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost:27017/mern_demo', {
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true,
});
mongoose.connection.on('connected', () => {
console.log('Connected to MongoDB');
});
// Start Server
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server started on port ${PORT}`);
});
- Create a directory routes and a file api.js inside it:
const express = require('express');
const router = express.Router();
// Define routes here
module.exports = router;
npx create-react-app client
cd client
npm install axios
- Create components for your application like List.js, Add.js, Edit.js.
- Use react-router-dom to define routes in App.js.
- In each component, implement CRUD operations using Axios to communicate with the backend API.
- Make HTTP requests from React components to the Express backend using Axios.
-
Backend Deployment Deploy your Express server to a cloud platform like Heroku or AWS Elastic Beanstalk.
-
Frontend Deployment Deploy your React app to platforms like Netlify, Vercel, or GitHub Pages.
This guide provides a basic structure for building a MERN stack application from scratch. You can further enhance it by adding authentication, authorization, validation, error handling, and other features based on your project requirements.
- Models (database schema)
- Authentication & Authorization
- Validation
- Error handling
- Some additional features.
- Create a User model in MongoDB using Mongoose.
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const bcrypt = require('bcryptjs');
const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
email: { type: String, unique: true, required: true },
password: { type: String, required: true },
role: { type: String, enum: ['user', 'admin'], default: 'user' }
});
userSchema.pre('save', async function(next) {
const user = this;
if (!user.isModified('password')) return next();
const hashedPassword = await bcrypt.hash(user.password, 10);
user.password = hashedPassword;
next();
});
userSchema.methods.comparePassword = async function(candidatePassword) {
return await bcrypt.compare(candidatePassword, this.password);
};
module.exports = mongoose.model('User', userSchema);
---- Implement routes for user registration, login, logout, and authentication using JWT (JSON Web Tokens) ----
- Use middleware to protect routes that require authentication.
- Implement role-based access control if needed.
const express = require('express');
const router = express.Router();
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
const User = require('../models/User');
router.post('/register', async (req, res) => {
try {
const { email, password } = req.body;
const user = new User({ email, password });
await user.save();
res.status(201).json({ message: 'User registered successfully' });
} catch (error) {
res.status(400).json({ error: error.message });
}
});
router.post('/login', async (req, res) => {
try {
const { email, password } = req.body;
const user = await User.findOne({ email });
if (!user) throw new Error('User not found');
const isMatch = await user.comparePassword(password);
if (!isMatch) throw new Error('Invalid credentials');
const token = jwt.sign({ userId: user._id }, 'secret', { expiresIn: '1h' });
res.status(200).json({ token });
} catch (error) {
res.status(401).json({ error: error.message });
}
});
module.exports = router;
- Implement validation for user input on the server-side using libraries like express-validator.
- Validate request bodies before processing.
const { validationResult } = require('express-validator');
const validate = (req, res, next) => {
const errors = validationResult(req);
if (!errors.isEmpty()) {
return res.status(400).json({ errors: errors.array() });
}
next();
};
module.exports = validate;
- Implement client-side validation using libraries like formik or plain JavaScript.
- Validate user input before submitting forms.
import React, { useState } from 'react';
const RegisterForm = () => {
const [formData, setFormData] = useState({
email: '',
password: ''
});
const [errors, setErrors] = useState({});
const handleChange = (e) => {
setFormData({ ...formData, [e.target.name]: e.target.value });
};
const handleSubmit = (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
// Perform client-side validation
if (!formData.email || !formData.password) {
setErrors({ message: 'Please fill in all fields' });
return;
}
// Send form data to backend
// ...
};
return (
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<input type="email" name="email" value={formData.email} onChange={handleChange} />
<input type="password" name="password" value={formData.password} onChange={handleChange} />
<button type="submit">Register</button>
{errors.message && <p>{errors.message}</p>}
</form>
);
};
export default RegisterForm;
- Implement centralized error handling middleware in Express to catch errors.
- Return appropriate error responses to the client with descriptive error messages.
Centralized Error Handling Middleware (backend/middleware/errorHandler.js)
const errorHandler = (err, req, res, next) => {
console.error(err.stack);
res.status(500).json({ message: 'Internal server error' });
};
module.exports = errorHandler;
- Handle errors returned from API requests on the client-side.
- Display error messages to users in a user-friendly manner.
const express = require('express');
const errorHandler = require('./middleware/errorHandler');
const app = express();
// Middleware
app.use(express.json());
app.use(errorHandler);
// Routes
app.use('/api/auth', require('./routes/auth'));
module.exports = app;
- Implement pagination for listing items (e.g., paginating through a list of products).
router.get('/products', async (req, res) => {
const page = parseInt(req.query.page) || 1;
const limit = parseInt(req.query.limit) || 10;
const skip = (page - 1) * limit;
try {
const products = await Product.find().skip(skip).limit(limit);
res.status(200).json(products);
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ error: error.message });
}
});
- Allow users to upload files (e.g., images) and store them in MongoDB using GridFS or a cloud - storage service like AWS S3.
const multer = require('multer');
const upload = multer({ dest: 'uploads/' });
router.post('/upload', upload.single('file'), (req, res) => {
const file = req.file;
if (!file) return res.status(400).json({ message: 'No file uploaded' });
// Process file and save to database
});
By incorporating authentication, authorization, validation, error handling, and additional >features into your MERN application, you can create a robust and secure web application that >meets the needs of your users. Remember to continuously iterate on your application, gather >feedback, and make improvements based on user requirements and best practices.