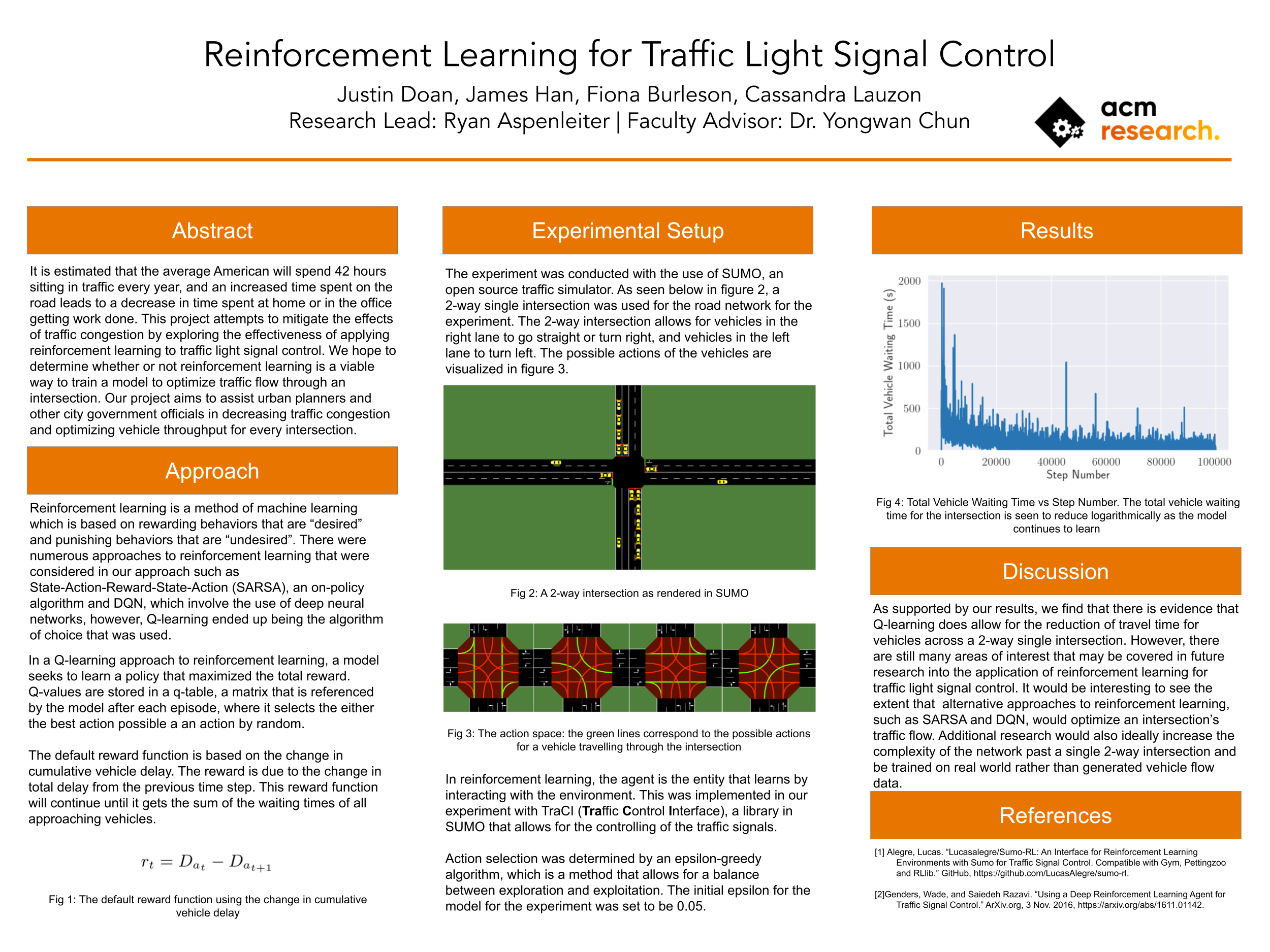
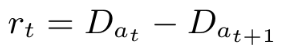It is estimated that the average american will lose about 97 hours every year as a result of traffic congestion, which has significant financial effects. If you take a look at this graph provided by INRIX (the world leader in mobility analytics), you can see that the congestion cost per driver, the cost of congestion which takes into account the increase in fuel wasted, negative effects of pollution, and other factors, has hit record highs and is only increasing. Our goal is to reduce this, to mitigate the effects of traffic congestion by exploring the effectiveness of applying reinforcement learning to traffic light signal control.
- Explore Reinforcement Learning Approaches
- Configure Simulation Environment
- Data preprocessing
- Model development and training
- Results Analysis
- We chose to apply reinforcement learning versus another method of machine learning because we can it’s very straightforward to reward a desired behavior that for example reduces vehicle wait time and punish an undesired behavior that increases vehicle wait time.
- There are numerous types of reinforcement learning, such as State-Action-Result-State-Action (SARSA) and Deep Q-Networks (DQN). However, Q-learning was chosen as method to apply.
- Form of reinforcement learning that seeks to learn a policy which maximizes the total reward
- Q values are stored in a Q-table, and are referenced by the model where it selects an action and stored the reward of that action
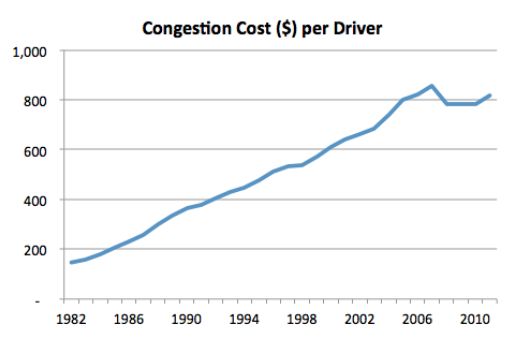
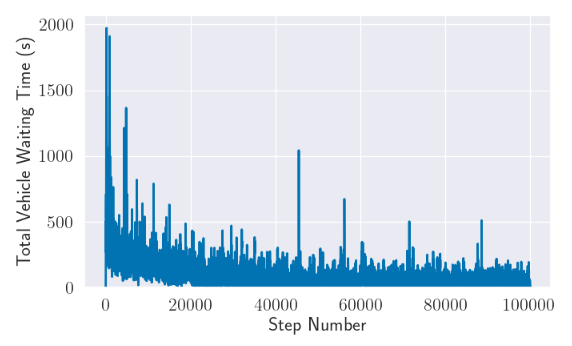
- The reward function that we used calculates the reward by calculating the change in cumulative vehicle delay
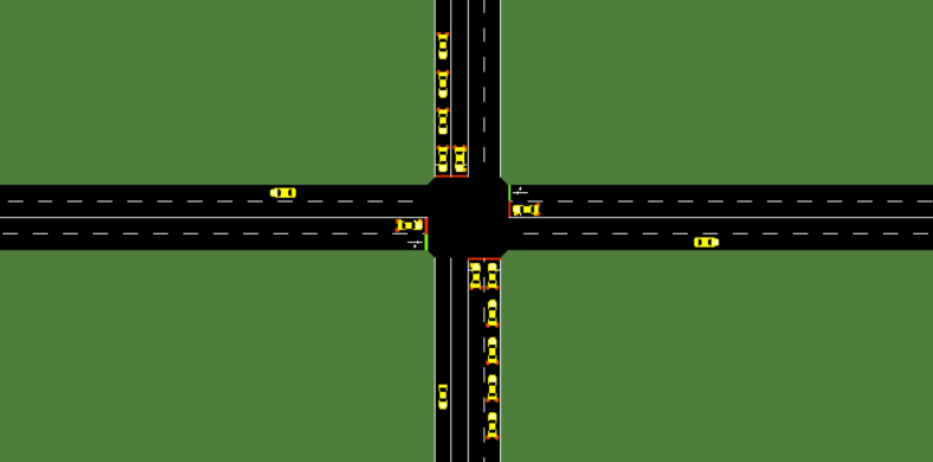
- Simulation of Urban MObility is an open source, portable, microscopic and continuous multi-modal traffic simulation package designed to handle large networks.
- It’s also cited as being traditionally used in traffic signal control studies, so we determined it was the best way to create our simulation environment.
Our initial goal was to have our model train on real world data and compare its optimizations to real world performances. However, there were too many difficulties in Data Preprocessing. There were too much missing data, issues with converting data to vehicle routes, and difficulty building the environment for the datasets. Because of these issues, we sticked with route generated data to train our model.
- Uses TraCI (Traffic Control Interface), a library in SUMO that allows for the controlling of the traffic signals
- Action selection determined by an epsilon-greedy algorithm (picture above)
- Balances exploration and exploitation
- Initial epsilon value for the experiment was set to be 0.05
- Explore alternative reinforcement learning methods (SARSA/DQN)
- Examine the performance of the model in comparison to real world data
- Experiment on more complex intersections (more lanes, intersections connected to one another, etc.)
- Fiona Burleson
- Justin Doan
- James Han
- Cassandra Lauzon
- Ryan Aspenleiter - Research Lead
- Dr. Yongwan Chun - Faculty Advisor