| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
|
给定一个下标从 0 开始的大小为 n * n 的矩阵 grid,其中每个单元格的值 grid[i][j] 要么是 正整数,要么是表示阻塞单元格的值 -1 。
你可以从一个非阻塞单元格移动到与其共享边的任何非阻塞单元格。
对于任何单元格 (i, j),我们定义其 远离程度 R[i][j] 如下:
- 如果单元格
(i, j)是 非阻塞 单元格,则R[i][j]是值grid[x][y]的总和,其中 没有 从 非阻塞 单元格(x, y)到单元格(i, j)的路径。 - 对于阻塞单元格,
R[i][j] == 0。
返回所有单元格的 R[i][j] 之和。
示例 1:
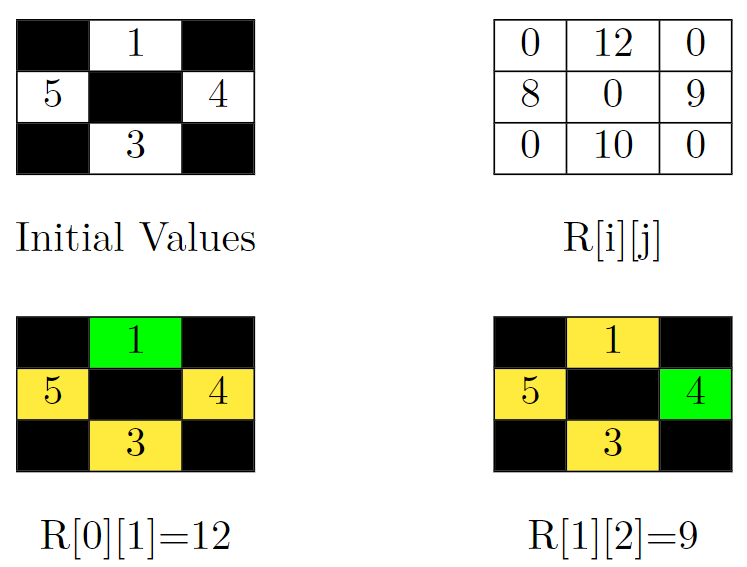
输入:grid = [[-1,1,-1],[5,-1,4],[-1,3,-1]] 输出:39 解释:在上面的图片中,有四个矩阵。左上角的矩阵是题目给定矩阵的初始值。被阻塞的单元格是黑色的,其他单元格的值与输入相同。在右上方的网格中,可以看到所有单元格的值也就是 R[i][j] 的值。答案是它们的和。即:0 + 12 + 0 + 8 + 0 + 9 + 0 + 10 + 0 = 39。 在上图左下角的矩阵,计算 R[0][1] (目标单元格为绿色)。我们应该将单元格 (0,1) 无法到达的单元格的值相加。这些单元格在这个矩阵中是黄色的。所以 R[0][1] = 5 + 4 + 3 = 12。 在上图右下角的矩阵,计算 R[1][2] (目标单元格为绿色)。我们应该把单元格 (1,2) 无法到达的单元格的值相加。这些单元格在这个矩阵中是黄色的。所以 R[1][2] = 1 + 5 + 3 = 9。
示例 2:
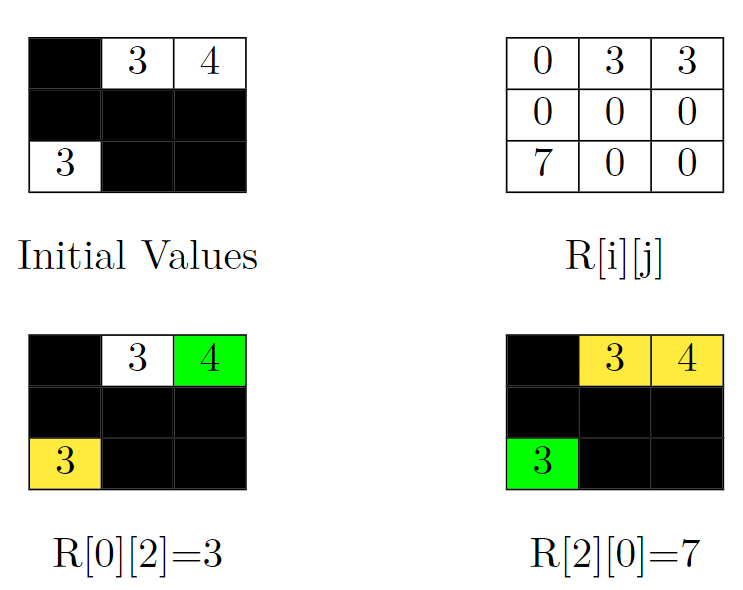
输入:grid = [[-1,3,4],[-1,-1,-1],[3,-1,-1]] 输出:13 解释:在上面的图片中,有四个矩阵。左上角的矩阵是给定矩阵的初始值。被阻塞的单元格是黑色的,其他单元格的值与输入相同。在右上方的网格中,可以看到所有单元格的值也就是 R[i][j] 的值。答案是它们的和。即:3 + 3 + 0 + 0 + 0 + 0 + 7 + 0 + 0 = 13。 在上图左下角的矩阵上,计算 R[0][2] (目标单元格为绿色)。将单元格 (0,2) 无法到达的单元格的值相加。这个单元格在这个矩阵中是黄色的。所以 R[0][2] = 3。 在上图右下角的矩阵上,计算 R[2][0] (目标单元格为绿色)。将单元格 (2,0) 无法到达的单元格的值相加,这些单元格在这个矩阵中是黄色的。所以 R[2][0] = 3 + 4 = 7。
示例 3:
输入:grid = [[1]] 输出:0 解释:因为除了 (0,0) 没有其他单元格,所以 R[0][0] 等于 0。所以所有单元格的和是 0。
提示:
1 <= n <= 3001 <= grid[i][j] <= 106或grid[i][j] == -1
我们先统计矩阵中非阻塞的格子的个数,记为
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def sumRemoteness(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def dfs(i: int, j: int) -> (int, int):
s, t = grid[i][j], 1
grid[i][j] = 0
for a, b in pairwise(dirs):
x, y = i + a, j + b
if 0 <= x < n and 0 <= y < n and grid[x][y] > 0:
s1, t1 = dfs(x, y)
s, t = s + s1, t + t1
return s, t
n = len(grid)
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
cnt = sum(x > 0 for row in grid for x in row)
ans = 0
for i, row in enumerate(grid):
for j, x in enumerate(row):
if x > 0:
s, t = dfs(i, j)
ans += (cnt - t) * s
return ansclass Solution {
private int n;
private int[][] grid;
private final int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
public long sumRemoteness(int[][] grid) {
n = grid.length;
this.grid = grid;
int cnt = 0;
for (int[] row : grid) {
for (int x : row) {
if (x > 0) {
++cnt;
}
}
}
long ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] > 0) {
long[] res = dfs(i, j);
ans += (cnt - res[1]) * res[0];
}
}
}
return ans;
}
private long[] dfs(int i, int j) {
long[] res = new long[2];
res[0] = grid[i][j];
res[1] = 1;
grid[i][j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] > 0) {
long[] tmp = dfs(x, y);
res[0] += tmp[0];
res[1] += tmp[1];
}
}
return res;
}
}class Solution {
public:
long long sumRemoteness(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
using pli = pair<long long, int>;
int n = grid.size();
int cnt = 0;
for (auto& row : grid) {
for (int x : row) {
cnt += x > 0;
}
}
int dirs[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
function<pli(int, int)> dfs = [&](int i, int j) {
long long s = grid[i][j];
int t = 1;
grid[i][j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] > 0) {
auto [ss, tt] = dfs(x, y);
s += ss;
t += tt;
}
}
return pli(s, t);
};
long long ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] > 0) {
auto [s, t] = dfs(i, j);
ans += (cnt - t) * s;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};func sumRemoteness(grid [][]int) (ans int64) {
n := len(grid)
cnt := 0
for _, row := range grid {
for _, x := range row {
if x > 0 {
cnt++
}
}
}
var dfs func(i, j int) (int, int)
dfs = func(i, j int) (int, int) {
s, t := grid[i][j], 1
grid[i][j] = 0
dirs := [5]int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1]
if x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] > 0 {
ss, tt := dfs(x, y)
s += ss
t += tt
}
}
return s, t
}
for i := range grid {
for j := range grid[i] {
if grid[i][j] > 0 {
s, t := dfs(i, j)
ans += int64(cnt-t) * int64(s)
}
}
}
return
}function sumRemoteness(grid: number[][]): number {
const n = grid.length;
let cnt = 0;
for (const row of grid) {
for (const x of row) {
if (x > 0) {
cnt++;
}
}
}
const dirs = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
const dfs = (i: number, j: number): [number, number] => {
let s = grid[i][j];
let t = 1;
grid[i][j] = 0;
for (let k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
const [x, y] = [i + dirs[k], j + dirs[k + 1]];
if (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] > 0) {
const [ss, tt] = dfs(x, y);
s += ss;
t += tt;
}
}
return [s, t];
};
let ans = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] > 0) {
const [s, t] = dfs(i, j);
ans += (cnt - t) * s;
}
}
}
return ans;
}