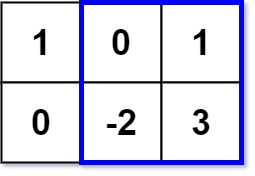
Given an m x n matrix matrix and an integer k, return the max sum of a rectangle in the matrix such that its sum is no larger than k.
It is guaranteed that there will be a rectangle with a sum no larger than k.
Example 1:
Input: matrix = [[1,0,1],[0,-2,3]], k = 2 Output: 2 Explanation: Because the sum of the blue rectangle [[0, 1], [-2, 3]] is 2, and 2 is the max number no larger than k (k = 2).
Example 2:
Input: matrix = [[2,2,-1]], k = 3 Output: 3
Constraints:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100-100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100-105 <= k <= 105
Follow up: What if the number of rows is much larger than the number of columns?
Companies:
Roblox, Google, Apple
Related Topics:
Array, Binary Search, Dynamic Programming, Matrix, Ordered Set
The brute force solution is enumerating O((MN)^2) all rectangles and for each rectangle sum the matrix sum in O(MN) time. The overall time complexity is O((MN)^3) which is too slow.
A better brute force is using prefix sum to save the O(MN) time calculating the matrix sum given a rectangle. The overall time complexity is O((MN)^2). Since M and N are at most 100, the time complexity is around O(10^8) which will still get TLE.
Now consider a single row matrix, we can scan the matrix from left to right and keep storing the prefix sums we've seen in a set. For the current prefix sum S, we want to find a prefix sum X from set that S - X <= K, i.e. X >= S - K. To find such a X, we can leverage lower_bound of set which takes O(logN) time. So this algorithm overall takes O(NlogN) time.
For a 2 x N matrix, how to find a 2-row submatrix with sum <= K? We can compress the matrix by summing each column individually.
2 1 -4
1 0 1
// after compression
3 1 -3
Then for this compressed (3 1 -3) vector, we can use the algorithm above for a single row matrix.
For a M x N matrix, we can enumerate different starting rows. For each starting row, we extend the bottom edge of the matrix continuously until it reaches the end. During this extention, we can keep compressing the matrix and running the algorithm for the compressed vector.
The overall time complexity is `O(M^2 * NlogN)
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/max-sum-of-rectangle-no-larger-than-k/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(M^2 * NlogN)
// Space: O(N)
class Solution {
public:
int maxSumSubmatrix(vector<vector<int>>& A, int k) {
int M = A.size(), N = A[0].size(), ans = INT_MIN;
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) { // starting row
vector<int> prefix(N, 0);
for (int j = i; j < M; ++j) { // ending row
int sum = 0;
set<int> s{0};
for (int t = 0; t < N; ++t) {
sum += A[j][t];
prefix[t] += sum;
int target = prefix[t + 1] - k;
auto it = s.lower_bound(target);
if (it != s.end()) {
ans = max(ans, prefix[t] - *it);
}
s.insert(prefix[t]);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};Or extract the maxSumSubarray function.
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/max-sum-of-rectangle-no-larger-than-k/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(M^2 * NlogN)
// Space: O(N)
class Solution {
int maxSumSubarray(vector<int> &A, int k) {
set<int> s{0};
int ans = INT_MIN;
for (int n : A) {
int target = n - k;
auto it = s.lower_bound(target);
if (it != s.end()) ans = max(ans, n - *it);
s.insert(n);
}
return ans;
}
public:
int maxSumSubmatrix(vector<vector<int>>& A, int k) {
int M = A.size(), N = A[0].size(), ans = INT_MIN;
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) { // starting row
vector<int> prefix(N, 0);
for (int j = i; j < M; ++j) { // ending row
int sum = 0;
for (int t = 0; t < N; ++t) {
sum += A[j][t];
prefix[t] += sum;
}
ans = max(ans, maxSumSubarray(prefix, k));
}
}
return ans;
}
};Considering the follow-up, the original algorithm is using O(M^2 * NlogN) time and M is always the number of rows.
If the number of rows is way larger than number of columns, we should transpose the matrix.
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/max-sum-of-rectangle-no-larger-than-k/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(min(M, N)^2 * max(M, N)log(max(M, N)))
// Space: O(max(M, N))
class Solution {
int maxSumSubarray(vector<int> &A, int k) {
set<int> s{0};
int ans = INT_MIN;
for (int n : A) {
int target = n - k;
auto it = s.lower_bound(target);
if (it != s.end()) ans = max(ans, n - *it);
s.insert(n);
}
return ans;
}
public:
int maxSumSubmatrix(vector<vector<int>>& A, int k) {
int M = A.size(), N = A[0].size(), ans = INT_MIN;
bool swapped = M > N;
if (swapped) swap(M, N);
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) { // starting row
vector<int> prefix(N, 0);
for (int j = i; j < M; ++j) { // ending row
int sum = 0;
for (int t = 0; t < N; ++t) {
sum += swapped ? A[t][j] : A[j][t];
prefix[t] += sum;
}
ans = max(ans, maxSumSubarray(prefix, k));
}
}
return ans;
}
};The maxSumSubarray function takes O(NlogN) time. We can use Kadane algorithm to get the maximum subarray sum in O(N) time, and if the maximum subarray sum is no more than k, we can directly return it.
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/max-sum-of-rectangle-no-larger-than-k/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(min(M, N)^2 * max(M, N)log(max(M, N)))
// Space: O(max(M, N))
class Solution {
int kadane(vector<int> &A) {
int ans = INT_MIN, mx = 0;
for (int n : A) {
mx = max(mx + n, n);
ans = max(ans, mx);
}
return ans;
}
int maxSumSubarray(vector<int> &A, int k) {
int maxKadane = kadane(A);
if (maxKadane <= k) return maxKadane;
set<int> s{0};
int ans = INT_MIN, sum = 0;
for (int n : A) {
sum += n;
int target = sum - k;
auto it = s.lower_bound(target);
if (it != s.end()) ans = max(ans, sum - *it);
s.insert(sum);
}
return ans;
}
public:
int maxSumSubmatrix(vector<vector<int>>& A, int k) {
int M = A.size(), N = A[0].size(), ans = INT_MIN;
bool swapped = M > N;
if (swapped) swap(M, N);
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) { // starting row
vector<int> sum(N, 0);
for (int j = i; j < M; ++j) { // ending row
for (int t = 0; t < N; ++t) sum[t] += swapped ? A[t][j] : A[j][t];
ans = max(ans, maxSumSubarray(sum, k));
}
}
return ans;
}
};