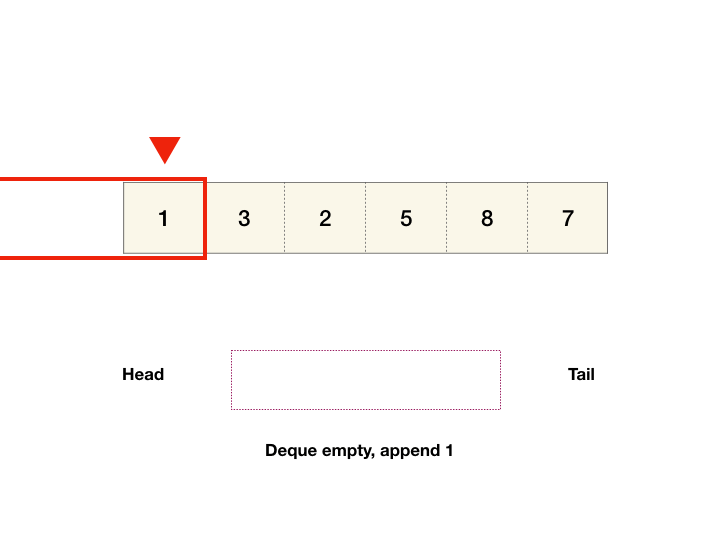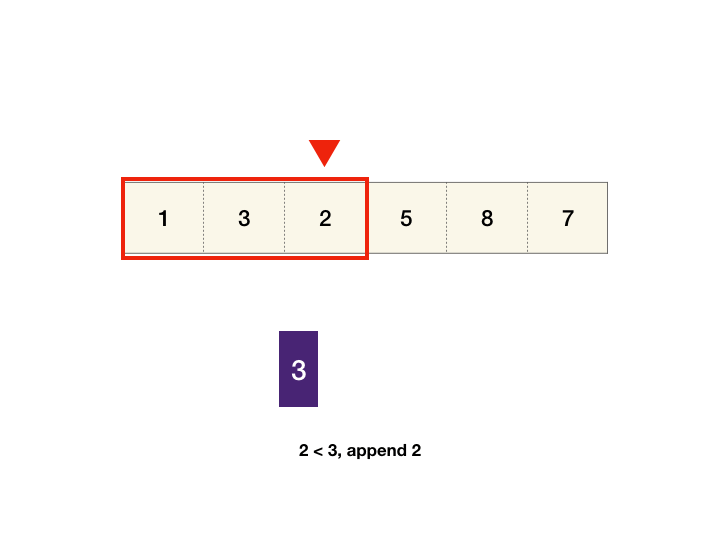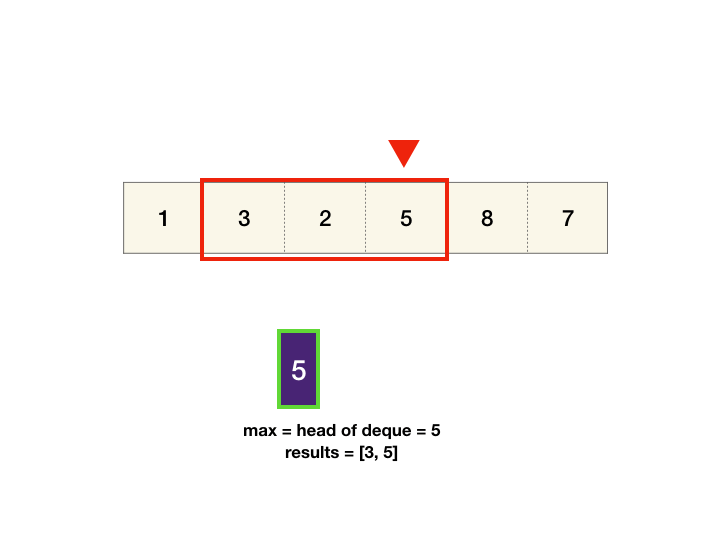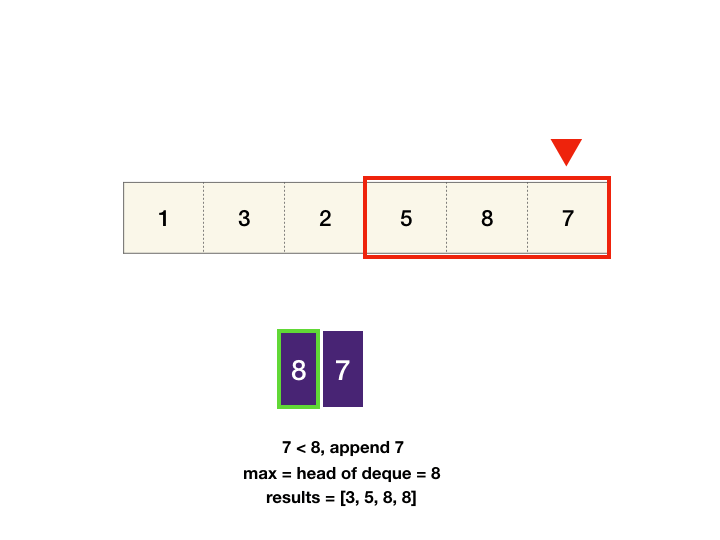
You are given an array of integers nums, there is a sliding window of size k which is moving from the very left of the array to the very right. You can only see the k numbers in the window. Each time the sliding window moves right by one position.
Return the max sliding window.
- For every window of size k we find the maximum element and add it in result vector.
- TC: O(n*k)
- We observe that if last element of window size is greatest then for next window of size k we don't need to check previous elements of window size k-1.
- We can maintain monotonic queue in which we store the max element index till now. i.e. queue: max->min element's index.
- If index at front of our queue is greater than window range, pop the front index from queue.
- if element at last index in queue is less than current element, pop the last index from queue.
- Now we have max element index in queue or queue is empty.
- push index i from back of queue. we get our max element index from front of queue.
- TC: O(n) Amortized
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k)
{
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> windowMax;
deque<int> dq;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// remove numbers from front which are out of window range k
while (!dq.empty() && dq.front() < i - (k - 1))
dq.pop_front();
// remove smaller numbers in k range as they are useless
while (!dq.empty() && nums[dq.back()] < nums[i])
dq.pop_back();
dq.push_back(i);
// if index is greater than first k elements
if (i >= k-1) windowMax.push_back(nums[dq.front()]);
}
return windowMax;
}
};