You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
Palace is an open-source, large-scale computational electromagnetic software package supported by the AWS Lab. It is feature-rich and capable of running on various high-performance hardware, supporting OpenMP, MPI, and GPU parallel computing. The use of the Apache open-source license is also highly advantageous. For more details, refer to the article 'Generating the solver input scripts of the computational electromagnetics software Palace using WELSIM'.
Although Palace is powerful, being a scientific computing program developed based on Linux, the official support for the Windows operating system is not complete. We have conducted research on the feasibility of running Palace on Windows, compiled Palace using Visual Studio, and generated a native Windows application with simulation results.
Palace provides the Superbuild compilation method with CMake, which automatically downloads all required libraries and compiles them completely. It compiles effortlessly on Linux. However, on Windows, many core libraries such as PETSc, SLEPc, libCEED, MUMPS, and others require manual compilation. Therefore, the Superbuild mode provided officially cannot compile as smoothly on Windows. Users need to apply the manual method of establishing Visual Studio projects to complete the building.
System and dependency libraries
Operating system: Windows 10, 64-bit
Compiler: Visual Studio 2022 Community, C++17. Intel Fortran Compiler 2022.
Palace version: 0.11.2
Dependency libraries:
Intel MKL: A popular linear algebra solver, using oneAPI 2022.2.0, consistent with the version of Fortran compiler.
METIS: A mesh partitioning tool for parallel computing, version 5.3.
Hypre: Computational package, version 2.52.
nlhmann/json: Modern C++-based JSON read-write package.
{fmt}: Formatting tool for input-output streams in C/C++.
Eigen: A well-known C++ numerical computing package, has no need for compilation; supports direct header file invocation.
libCEED: A linear algebra computation management terminal that supports parallel computing on various CPUs, GPUs, and clusters.
SuperLU_DIST: The parallel version of SuperLU, a sparse direct linear algebra solver library.
STRUMPACK: An open-source software library for large-scale sparse matrix computing.
MUMPS: An open-source software library from France for solving large-scale sparse linear systems.
SLEPc: A complex number linear algebra solver for eigenvalue problems, based on PETSc.
ARPACK-NG: A complex number linear algebra solver for eigenvalue problems, programmed using Fortran 77 langauge.
GSLIB: An interpolation sovler for high-order spectral elements, optional.
Among these, at least one of the three optional linear solvers SuperLU_DIST, STRUMPACK, MUMPS must be present. This article uses MUMPS. Additionally, out of the two complex solvers, SLEPc and ARPACK, at least one is required. Without them, eigenvalue-related computing cannot be performed. This article uses ARPACK.
Visual studio projects
Establish two projects, namely the static library project libpalace, and the executable file project palace. libpalace contains all header and source files. palace is the final generated executable file, containing only a main.cpp file. This is shown in the figure.
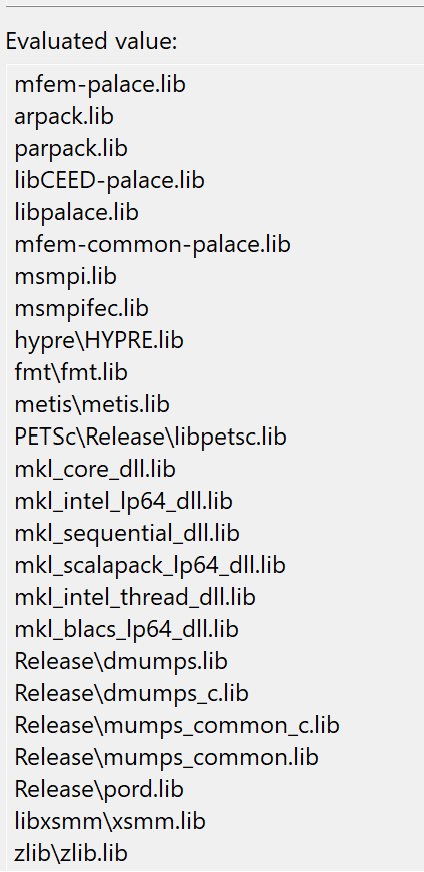
The method to add external header files and preprocessor macros is essentially the same as libpalace, so it will not be repeated here. Compiling the executable program requires linking all dependent libraries. The added linked libraries are as follows,
After building, place all dependent dynamic libraries (*.dll files) together with the palace.exe to run Palace. Test the executable program by running it on the Windows console.
You can also use the mpiexec command for MPI parallel computing. GPU parallel computing should also be feasible and will be discussed in future articles.
To contribute to simulation and the open-source communities, we have open-sourced the building files for Palace, shared at https://github.com/WelSimLLC/palace, and provided the compiled palace.exe executable file for users to use directly.
Conclusion
There are not many available open-source electromagnetic simulation solvers, and Palace provides powerful computing capabilities while also having a very friendly open-source license. WELSIM has become the first developer in the world to successfully compile Palace on Windows and open-source the building methods and files.
Some of Palace's dependency libraries that also face challenges when building on Windows will be discussed in future articles.
WelSim is not affiliated with Palace and Visual Studio. The development team and organization behind Palace and Visual Studio have no connection to WelSim. This reference is used here solely for the purpose of a technical blog article and software usage.
reacted with thumbs up emoji reacted with thumbs down emoji reacted with laugh emoji reacted with hooray emoji reacted with confused emoji reacted with heart emoji reacted with rocket emoji reacted with eyes emoji
-
Palace is an open-source, large-scale computational electromagnetic software package supported by the AWS Lab. It is feature-rich and capable of running on various high-performance hardware, supporting OpenMP, MPI, and GPU parallel computing. The use of the Apache open-source license is also highly advantageous. For more details, refer to the article 'Generating the solver input scripts of the computational electromagnetics software Palace using WELSIM'.

Although Palace is powerful, being a scientific computing program developed based on Linux, the official support for the Windows operating system is not complete. We have conducted research on the feasibility of running Palace on Windows, compiled Palace using Visual Studio, and generated a native Windows application with simulation results.
Palace provides the Superbuild compilation method with CMake, which automatically downloads all required libraries and compiles them completely. It compiles effortlessly on Linux. However, on Windows, many core libraries such as PETSc, SLEPc, libCEED, MUMPS, and others require manual compilation. Therefore, the Superbuild mode provided officially cannot compile as smoothly on Windows. Users need to apply the manual method of establishing Visual Studio projects to complete the building.
System and dependency libraries
Operating system: Windows 10, 64-bit
Compiler: Visual Studio 2022 Community, C++17. Intel Fortran Compiler 2022.
Palace version: 0.11.2
Dependency libraries:
Among these, at least one of the three optional linear solvers SuperLU_DIST, STRUMPACK, MUMPS must be present. This article uses MUMPS. Additionally, out of the two complex solvers, SLEPc and ARPACK, at least one is required. Without them, eigenvalue-related computing cannot be performed. This article uses ARPACK.
Visual studio projects
Establish two projects, namely the static library project libpalace, and the executable file project palace. libpalace contains all header and source files. palace is the final generated executable file, containing only a main.cpp file. This is shown in the figure.
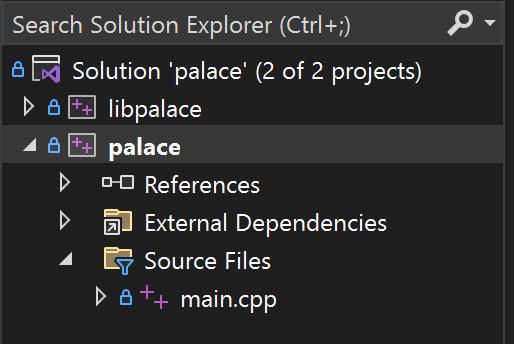
Project libpalace
Set the external header file directories.
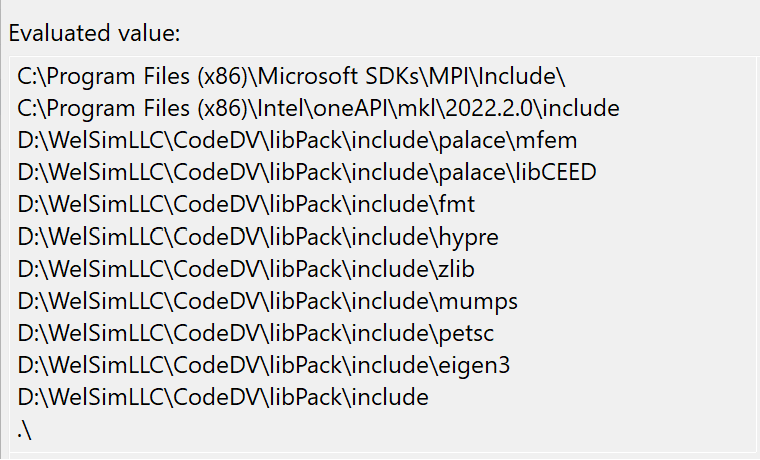
Add preprocessor macros:
CEED_SKIP_VISIBILITY PALACE_WITH_ARPACK _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGSProject palace
The method to add external header files and preprocessor macros is essentially the same as libpalace, so it will not be repeated here. Compiling the executable program requires linking all dependent libraries. The added linked libraries are as follows,
After building, place all dependent dynamic libraries (*.dll files) together with the palace.exe to run Palace. Test the executable program by running it on the Windows console.
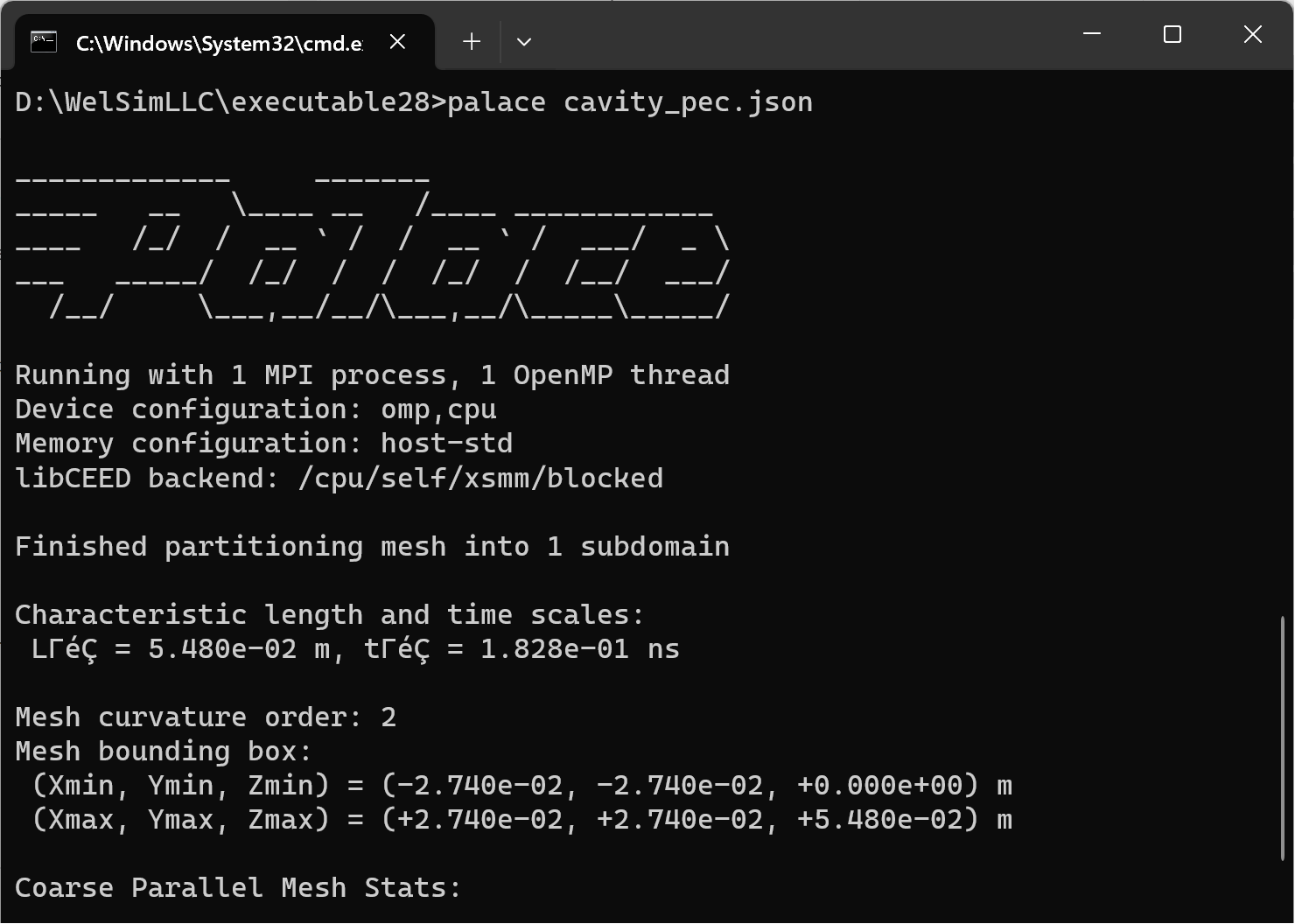
You can also use the mpiexec command for MPI parallel computing. GPU parallel computing should also be feasible and will be discussed in future articles.
To contribute to simulation and the open-source communities, we have open-sourced the building files for Palace, shared at https://github.com/WelSimLLC/palace, and provided the compiled palace.exe executable file for users to use directly.
Conclusion
There are not many available open-source electromagnetic simulation solvers, and Palace provides powerful computing capabilities while also having a very friendly open-source license. WELSIM has become the first developer in the world to successfully compile Palace on Windows and open-source the building methods and files.
Some of Palace's dependency libraries that also face challenges when building on Windows will be discussed in future articles.
WelSim is not affiliated with Palace and Visual Studio. The development team and organization behind Palace and Visual Studio have no connection to WelSim. This reference is used here solely for the purpose of a technical blog article and software usage.
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
All reactions