You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
An Automated Regression Testing System is a vital component for all large software products. It's used to verify the software will continue to function properly even after the source code has been modified. It is a critical part of the software development and testing lifecycle, allowing developers to continuously enhance the software without compromising its functionality. Engineering simulation software, also called Computer Aided Engineering (CAE) software, is characterized by its large scale, wide scope, and lengthy lifetime. The necessity of a comprehensive automated regression testing system is dictated by these attributes to ensure the stability and accuracy of the product.
At present, almost all CAE software is separate from the testing system, and end-users generally do not interact with the testing system. However, developers of CAE software must have a clear understanding of the construction and maintenance of the entire automated testing system to effectively apply the testing tools and ensure the quality of the software product. WELSIM is the world's first CAE software that provides an automated testing system to end-users and has open-sourced all testing cases. This article provides a detailed description of the application philosophy and practice of automated regression testing in large-scale general-purpose simulation CAE software.
Why Automated Regression Testing
While regression testing can be done manually, it is error-prone and inefficient. This approach may work occasionally when the software is small, but as the software becomes larger and requires collaboration among multiple individuals, automation becomes necessary. Regression testing ensures that CAE software products continue to perform existing functions accurately, after any changes or modifications.
The reasons for changes in CAE software are generally classified into four main categories:
(1) Adding new features: This is the most common reason to run regression testing, as new and old code must be fully compatible. When developers introduce new code, they might overlook existing code developed years ago. In such cases, regression testing is necessary to uncover potential issues. For example, adding a control parameter for mesh generation to WELSIM might affect existing parameters. Regression testing in this situation can uncover hidden problems.
(2) Functional modifications: During the early stages of product development, developers often modify existing features, either discarding or changing certain aspects of it. In such cases, regression testing can verify whether related features have been deleted or modified, ensuring that other functions have not been compromised.
(3) Integration of features: In this scenario, regression testing ensures that the software product works seamlessly after integration with other products. For instance, when integrating the fluid-structure coupling functionality in CAE, new code might impact existing structural modules or fluid module features. Automated testing can promptly detect any issues.
(4) Defect and issue fixes: This is the most frequently encountered situation. For large software like CAE, the developers' efforts to fix discovered bugs might inadvertently introduce more. Therefore, regression testing is crucial to maintain software quality.
Types of Regression Testing for CAE Software
Due to the broad scope of CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering), regression testing needs to cover a wide range of areas. Based on years of firsthand experience in developing WELSIM, we have summarized common regression testing types for CAE simulation software:
Graphical User Interface (GUI) Testing
Modern simulation software often includes very complex functionalities, so GUI testing is a crucial aspect to ensure software stability and simplicity. This involves testing various interactive controls such as menus, toolbars, tree structures, property windows, pop-up menus, dialogue boxes, and three-dimensional graphical display windows with detailed interactive features. User interface testing ensures a visually appealing application, and it often ensures the user-friendliness of the product in advance. For the design of windows in large CAE software, you can refer to the article "Window design and development for general-purpose simulation software."
Compatibility Testing
CAE software can be used on different types of hardware and operating systems. So, the testing system needs to support mainstream hardware systems and common operating systems like Windows and Linux. This requires developers to have a certain number of hardware systems, or even virtual machines, to conduct compatibility testing in various user environments before major version releases. The automated testing maintenance system needs to accommodate the supported operating systems. For cloud-based CAE applications, testing different web browsers and network environments is necessary.
Numerical Accuracy Testing
Unlike other types of software, engineering simulation CAE software places a high demand on the accuracy of computational results. Accuracy is also a crucial metric for assessing simulation software. Therefore, numerical accuracy testing is an essential part of the testing system. Common validation methods involve checking the maximum and minimum values of results, such as the maximum and minimum stress values in structural analysis, or the maximum and minimum velocity results in fluid analysis. Single values can also be validated, such as the total energy value in dynamic systems. Due to hardware and operating system variations, a certain degree of error is allowed in the results, typically not exceeding 5%.
Data Persistence Testing
Data persistence testing is relatively difficult in the testing system, so it requires developers to have a deep understanding of the product. After continuous updates, it needs to be ensured the new project is compatible with project files from older versions. Modern CAE software is updated frequently; therefore, guaranteeing that persistent project data from at least the last three years can be read and converted is sufficient. From a maintenance cost reduction perspective, there is no need to support project files from a very long time ago.
In addition to these, there are other essential testing aspects such as security testing, localization and globalization testing, memory stress testing, etc. Due to space limitations, these aspects are not elaborated here.
Maintenance of Test Cases
The test repository, a crucial part of the testing system, requires continuous maintenance. CAE software is frequently modified and new versions are continuously released. Modified new versions might introduce new features or changes in software functionality. In such cases, certain test cases might become obsolete, necessitating maintenance. Often, new test cases need to be added to test new features or characteristics.
Maintenance of CAE test cases is an ongoing process. The software development baseline is typically used as a reference point. Maintenance primarily involves the following aspects: (1) Removing outdated test cases. (2) Enhancing uncontrolled test cases. (3) Deleting redundant test cases. (4) Adding new test cases.
Maintaining the test cases is a substantial and long-term effort that requires significant resources. Hence, no mature CAE software company has shared the test cases. However, WELSIM has open-sourced all test cases, contributing to the simulation community.
Test Report Generation
Test results need to be easily read for users. With the growth of CAE software's automated test cases over time and with added features, having thousands or tens of thousands of test cases is common. Test reports are generated automatically; they prominently list failed test cases while also providing an overall test pass rate. Test results are output in lightweight formats, like XML or JSON, for display on the user side or deployment in the cloud. This enables teams and clients to view the test results of the current software version. Test result files can include the machine name and time tags, as well as other information to help users access historical testing data.
Running Regression Test
Although automated testing is highly efficient and test case scripting can be refined, running automated regression tests can be costly. As the number of test cases increases, each test running requires more time and resources. The more tests you run, the higher the expense. When a product is about to be released, or when significant features are added or widespread changes are made, it's necessary to run regression tests intensively. Experienced programmers have a clear understanding of their code modifications. So, they can decide whether to run all test cases, run only a subset of quick tests, or skip regression testing altogether for specific changes.
WELSIM's Automated Testing System
The general-purpose engineering simulation CAE software, WELSIM, has undergone several years of development and its product has reached a stable state. Recently, the automated testing system has been made accessible to end-users, along with open-sourcing all of its test cases. Users not only have the ability to run validated test cases on their local machines, but to also quickly create their own test cases. Currently, WELSIM primarily uses XML as its test file format. The automated testing feature supports both Windows and Linux versions.
Running automated tests in WELSIM is straightforward. From the menu bar, simply select Tools → Play Test…, follow the prompts to select the desired test cases (multiple selections are supported), and click "Run" to initiate the automated testing. The testing process requires no manual intervention.
Creating test cases is also simplified. From the menu bar, select Tools → Record Test…, choose a name for the saved test file as prompted; then use the GUI to record the test case.
Once a recording is complete, the XML test file can be opened using a text editor to review the test steps and manually adjust and simplify the steps if needed.
WELSIM has open-sourced all its test cases and will maintain them long-term, contributing to the simulation community.
Conclusion
From a technical perspective, an automated testing system is a combination of software macros and data persistence. However, developing an automated regression system for engineering simulation CAE software requires an understanding of the underlying logic of user interface frameworks and a clear comprehension of various physical engineering analysis cases. Only with this knowledge can a comprehensive system be created and maintained successfully.
Building upon years of dedicated CAE software development, WELSIM directly offers its automated testing system to users. Users can run a variety of tests on their local machines and create test cases that align with their interests. For developers working on solvers or grid generators, utilizing WELSIM to construct an automated testing system significantly reduces the time and resources required for developing their own testing systems. This has a positive impact on the entire engineering simulation community. At present, WELSIM seamlessly supports several well-known open-source solvers such as FrontISTR, OpenRadioss, SU2, among others. More open-source solvers are continually being supported.
This article primarily focuses on describing automated regression testing for CAE software, but the discussed methods and practices can also be applied to other large-scale software systems.
WELSIM is the #1 engineering simulation software for the open-source community.
reacted with thumbs up emoji reacted with thumbs down emoji reacted with laugh emoji reacted with hooray emoji reacted with confused emoji reacted with heart emoji reacted with rocket emoji reacted with eyes emoji
-
An Automated Regression Testing System is a vital component for all large software products. It's used to verify the software will continue to function properly even after the source code has been modified. It is a critical part of the software development and testing lifecycle, allowing developers to continuously enhance the software without compromising its functionality. Engineering simulation software, also called Computer Aided Engineering (CAE) software, is characterized by its large scale, wide scope, and lengthy lifetime. The necessity of a comprehensive automated regression testing system is dictated by these attributes to ensure the stability and accuracy of the product.
At present, almost all CAE software is separate from the testing system, and end-users generally do not interact with the testing system. However, developers of CAE software must have a clear understanding of the construction and maintenance of the entire automated testing system to effectively apply the testing tools and ensure the quality of the software product. WELSIM is the world's first CAE software that provides an automated testing system to end-users and has open-sourced all testing cases. This article provides a detailed description of the application philosophy and practice of automated regression testing in large-scale general-purpose simulation CAE software.
Why Automated Regression Testing
While regression testing can be done manually, it is error-prone and inefficient. This approach may work occasionally when the software is small, but as the software becomes larger and requires collaboration among multiple individuals, automation becomes necessary. Regression testing ensures that CAE software products continue to perform existing functions accurately, after any changes or modifications.
The reasons for changes in CAE software are generally classified into four main categories:
(1) Adding new features: This is the most common reason to run regression testing, as new and old code must be fully compatible. When developers introduce new code, they might overlook existing code developed years ago. In such cases, regression testing is necessary to uncover potential issues. For example, adding a control parameter for mesh generation to WELSIM might affect existing parameters. Regression testing in this situation can uncover hidden problems.
(2) Functional modifications: During the early stages of product development, developers often modify existing features, either discarding or changing certain aspects of it. In such cases, regression testing can verify whether related features have been deleted or modified, ensuring that other functions have not been compromised.
(3) Integration of features: In this scenario, regression testing ensures that the software product works seamlessly after integration with other products. For instance, when integrating the fluid-structure coupling functionality in CAE, new code might impact existing structural modules or fluid module features. Automated testing can promptly detect any issues.
(4) Defect and issue fixes: This is the most frequently encountered situation. For large software like CAE, the developers' efforts to fix discovered bugs might inadvertently introduce more. Therefore, regression testing is crucial to maintain software quality.
Types of Regression Testing for CAE Software
Due to the broad scope of CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering), regression testing needs to cover a wide range of areas. Based on years of firsthand experience in developing WELSIM, we have summarized common regression testing types for CAE simulation software:
Graphical User Interface (GUI) Testing
Modern simulation software often includes very complex functionalities, so GUI testing is a crucial aspect to ensure software stability and simplicity. This involves testing various interactive controls such as menus, toolbars, tree structures, property windows, pop-up menus, dialogue boxes, and three-dimensional graphical display windows with detailed interactive features. User interface testing ensures a visually appealing application, and it often ensures the user-friendliness of the product in advance. For the design of windows in large CAE software, you can refer to the article "Window design and development for general-purpose simulation software."
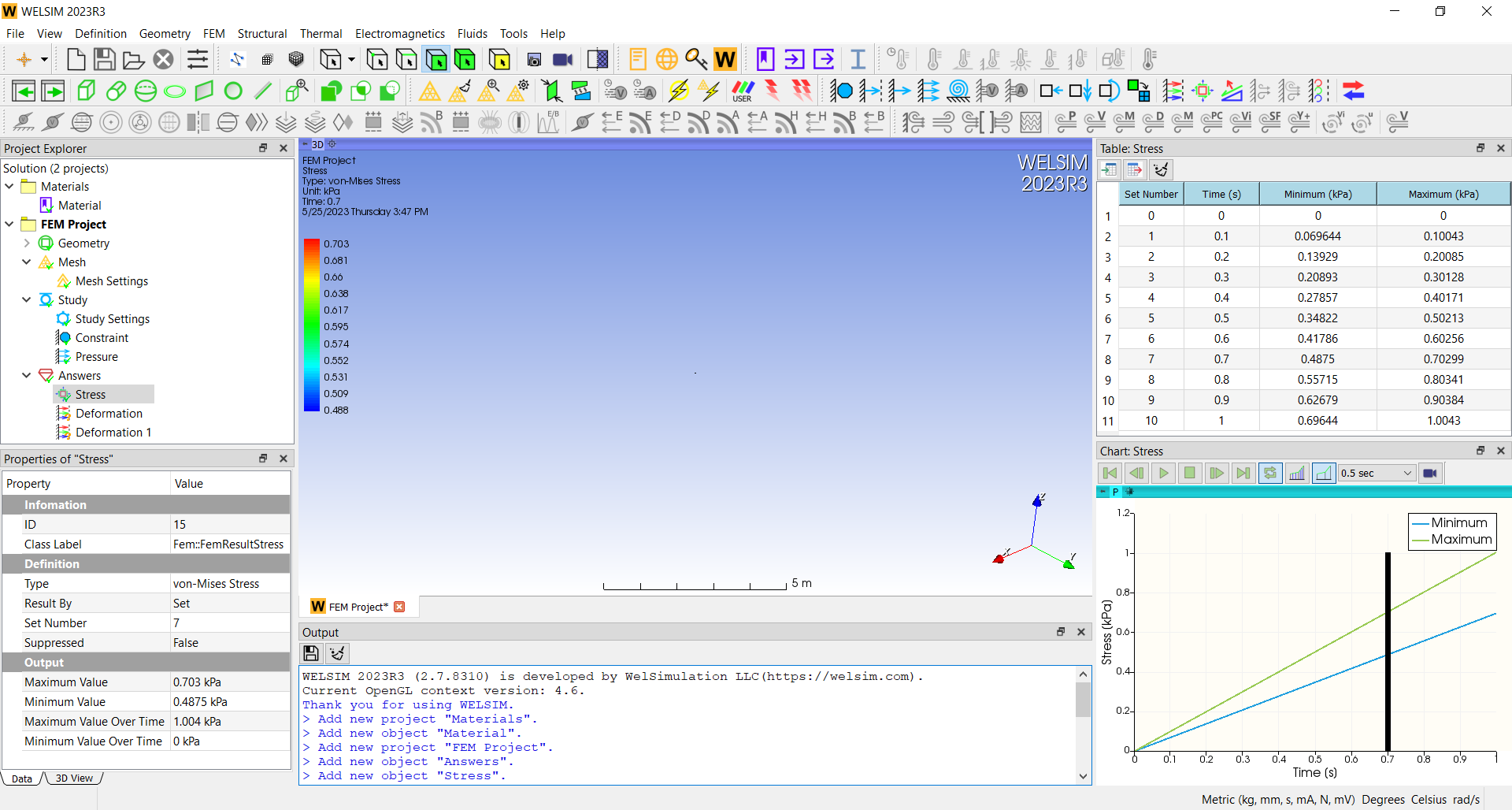
Compatibility Testing
CAE software can be used on different types of hardware and operating systems. So, the testing system needs to support mainstream hardware systems and common operating systems like Windows and Linux. This requires developers to have a certain number of hardware systems, or even virtual machines, to conduct compatibility testing in various user environments before major version releases. The automated testing maintenance system needs to accommodate the supported operating systems. For cloud-based CAE applications, testing different web browsers and network environments is necessary.
Numerical Accuracy Testing
Unlike other types of software, engineering simulation CAE software places a high demand on the accuracy of computational results. Accuracy is also a crucial metric for assessing simulation software. Therefore, numerical accuracy testing is an essential part of the testing system. Common validation methods involve checking the maximum and minimum values of results, such as the maximum and minimum stress values in structural analysis, or the maximum and minimum velocity results in fluid analysis. Single values can also be validated, such as the total energy value in dynamic systems. Due to hardware and operating system variations, a certain degree of error is allowed in the results, typically not exceeding 5%.
Data Persistence Testing
Data persistence testing is relatively difficult in the testing system, so it requires developers to have a deep understanding of the product. After continuous updates, it needs to be ensured the new project is compatible with project files from older versions. Modern CAE software is updated frequently; therefore, guaranteeing that persistent project data from at least the last three years can be read and converted is sufficient. From a maintenance cost reduction perspective, there is no need to support project files from a very long time ago.
In addition to these, there are other essential testing aspects such as security testing, localization and globalization testing, memory stress testing, etc. Due to space limitations, these aspects are not elaborated here.
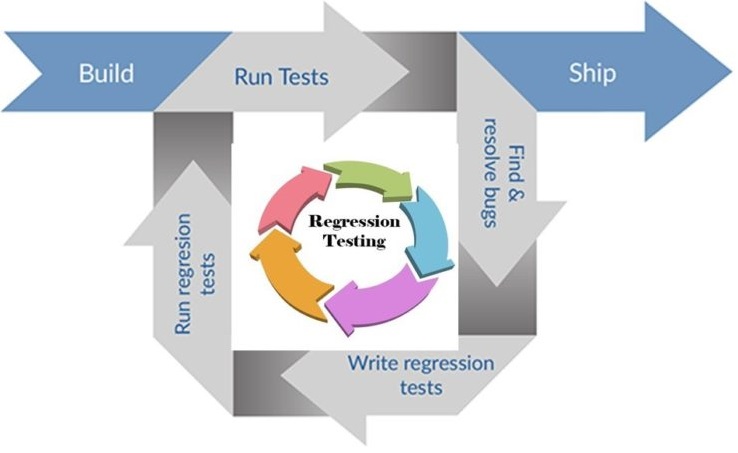
Maintenance of Test Cases
The test repository, a crucial part of the testing system, requires continuous maintenance. CAE software is frequently modified and new versions are continuously released. Modified new versions might introduce new features or changes in software functionality. In such cases, certain test cases might become obsolete, necessitating maintenance. Often, new test cases need to be added to test new features or characteristics.
Maintenance of CAE test cases is an ongoing process. The software development baseline is typically used as a reference point. Maintenance primarily involves the following aspects: (1) Removing outdated test cases. (2) Enhancing uncontrolled test cases. (3) Deleting redundant test cases. (4) Adding new test cases.
Maintaining the test cases is a substantial and long-term effort that requires significant resources. Hence, no mature CAE software company has shared the test cases. However, WELSIM has open-sourced all test cases, contributing to the simulation community.

Test Report Generation
Test results need to be easily read for users. With the growth of CAE software's automated test cases over time and with added features, having thousands or tens of thousands of test cases is common. Test reports are generated automatically; they prominently list failed test cases while also providing an overall test pass rate. Test results are output in lightweight formats, like XML or JSON, for display on the user side or deployment in the cloud. This enables teams and clients to view the test results of the current software version. Test result files can include the machine name and time tags, as well as other information to help users access historical testing data.
Running Regression Test
Although automated testing is highly efficient and test case scripting can be refined, running automated regression tests can be costly. As the number of test cases increases, each test running requires more time and resources. The more tests you run, the higher the expense. When a product is about to be released, or when significant features are added or widespread changes are made, it's necessary to run regression tests intensively. Experienced programmers have a clear understanding of their code modifications. So, they can decide whether to run all test cases, run only a subset of quick tests, or skip regression testing altogether for specific changes.
WELSIM's Automated Testing System
The general-purpose engineering simulation CAE software, WELSIM, has undergone several years of development and its product has reached a stable state. Recently, the automated testing system has been made accessible to end-users, along with open-sourcing all of its test cases. Users not only have the ability to run validated test cases on their local machines, but to also quickly create their own test cases. Currently, WELSIM primarily uses XML as its test file format. The automated testing feature supports both Windows and Linux versions.
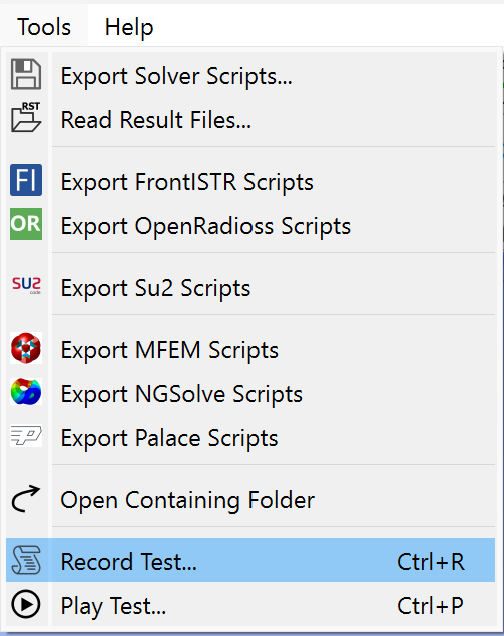
Running automated tests in WELSIM is straightforward. From the menu bar, simply select Tools → Play Test…, follow the prompts to select the desired test cases (multiple selections are supported), and click "Run" to initiate the automated testing. The testing process requires no manual intervention.
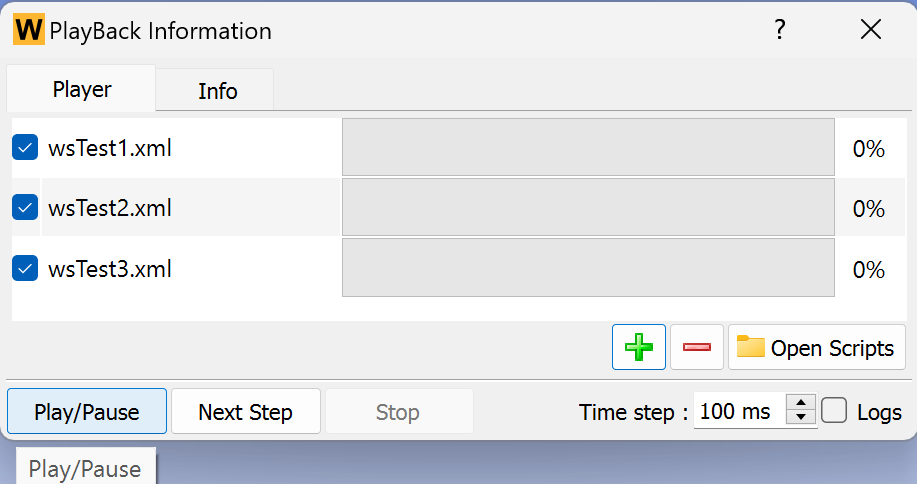
Creating test cases is also simplified. From the menu bar, select Tools → Record Test…, choose a name for the saved test file as prompted; then use the GUI to record the test case.
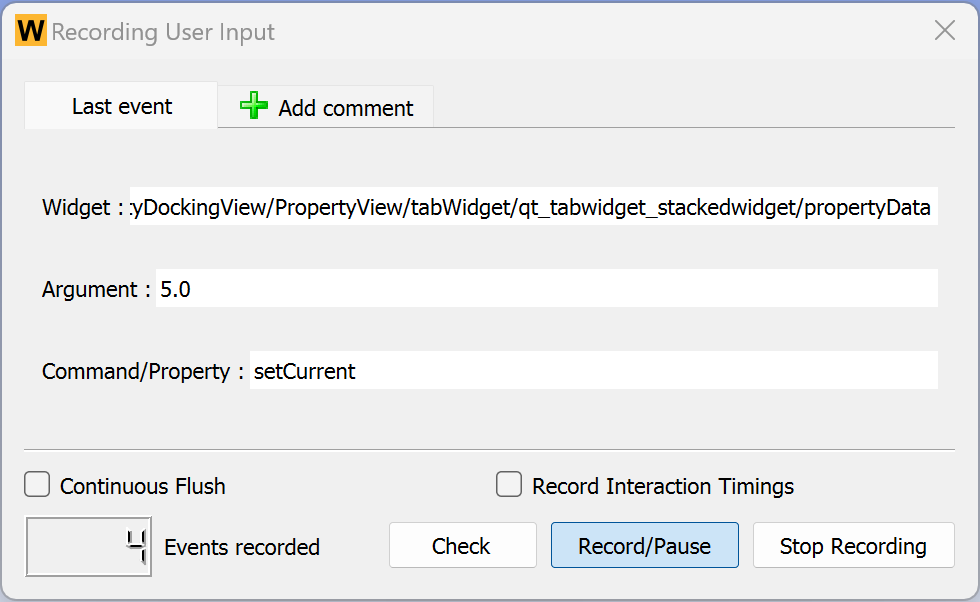
Once a recording is complete, the XML test file can be opened using a text editor to review the test steps and manually adjust and simplify the steps if needed.
WELSIM has open-sourced all its test cases and will maintain them long-term, contributing to the simulation community.
Conclusion
From a technical perspective, an automated testing system is a combination of software macros and data persistence. However, developing an automated regression system for engineering simulation CAE software requires an understanding of the underlying logic of user interface frameworks and a clear comprehension of various physical engineering analysis cases. Only with this knowledge can a comprehensive system be created and maintained successfully.
Building upon years of dedicated CAE software development, WELSIM directly offers its automated testing system to users. Users can run a variety of tests on their local machines and create test cases that align with their interests. For developers working on solvers or grid generators, utilizing WELSIM to construct an automated testing system significantly reduces the time and resources required for developing their own testing systems. This has a positive impact on the entire engineering simulation community. At present, WELSIM seamlessly supports several well-known open-source solvers such as FrontISTR, OpenRadioss, SU2, among others. More open-source solvers are continually being supported.
This article primarily focuses on describing automated regression testing for CAE software, but the discussed methods and practices can also be applied to other large-scale software systems.
WELSIM is the #1 engineering simulation software for the open-source community.
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
All reactions