QuOptimalControl is superseded by QuantumControl.jl
Trying to mimic the interface that DifferentialEquations.jl uses we offer several problem definitions. Problems define the dynamics of the quantum system.
Once a problem has been constructed we can use any of the available algorithms (ADGRAPE, GRAPE and dCRAB) to solve the problem. Using multiple dispatch the solver should then get to work.
using QuantumInformation # provides Pauli matrices for example
ρinit = [1.0 0.0]' * [1.0 0.0 + 0im]
ρfin = [0.0 1.0]' * [0.0 1.0 + 0im]
prob = Problem(
B = [sx, sy],
A = [0.0 * sz],
Xi = [ρ1],
Xt = [ρt],
T = 1.0,
n_controls = 2,
guess = rand(2, 10),
sys_type = StateTransfer()
)
sol = solve(prob)And in this case our chosen algorithm, the approximate GRAPE algorithm, will solve the problem automatically, there's no need to define anything else!
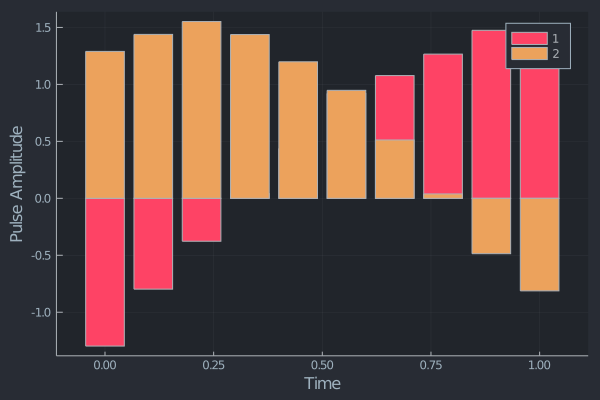
Now we can visualise the output pulse:
visualise_pulse(sol.opti_pulses, duration = prob.T)Using Julia's package manager QuOptimalControl.jl is easy to install and use!
] add https://github.com/alastair-marshall/QuOptimalControl.jlCurrently the package supports both an analytical gradient based GRAPE optimiser, a new automatic differentiation based version of GRAPE (using Zygote) and a dCRAB (gradient free optimiser). For the defined problem types within the package (ClosedStateTransfer, UnitarySynthesis, OpenSystemCoherenceTransfer, ExperimentInterface) there are several predefined solver methods to make it easy to construct and solve common problems.